Top 5 Collagen Supplement Myths – Debunked with Science
Think collagen supplements are just hype? We break down the top 5 collagen supplement myths and reveal what science really says about them.
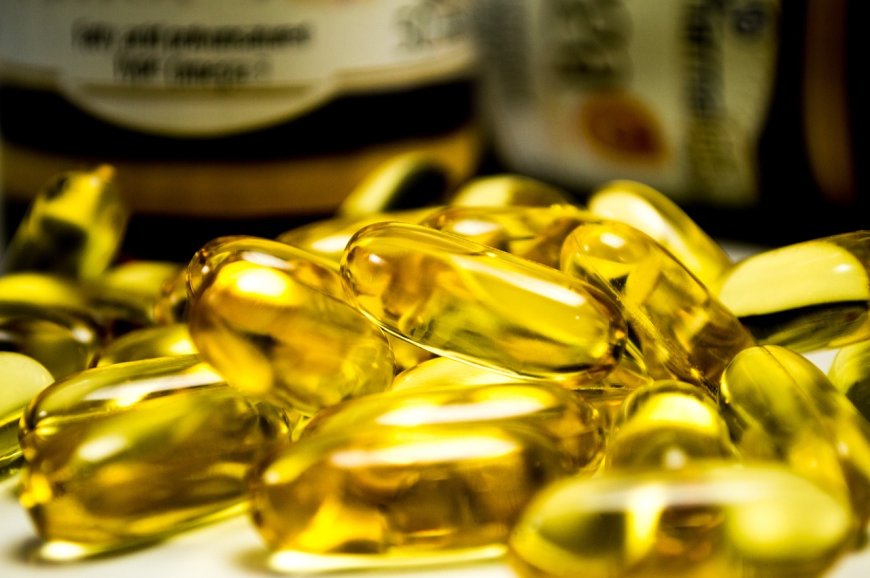

Collagen supplements have taken the wellness world by storm. From skin elasticity to joint support, they’re everywhere—from fitness influencers to beauty gurus. But with popularity comes plenty of misinformation. Are they really the fountain of youth—or just another marketing fad?
Let’s break down the top collagen supplement myths and get to the truth backed by science, not speculation.
1. Myth: Collagen Supplements Don't Work
One of the most common misconceptions is that collagen supplements are ineffective because the body breaks them down during digestion. While it’s true that collagen is broken into peptides and amino acids in the gut, this doesn't make them useless.
The Truth:
Research shows that collagen peptides can be absorbed and used by the body to stimulate natural collagen production. A 2019 study published in Nutrients found that participants who took hydrolyzed collagen daily saw improved skin elasticity and hydration after just 8 weeks.
✅ Key takeaway: Collagen supplements do get broken down—but they still deliver results.
2. Myth: All Collagen Is the Same
Many assume that collagen supplements are one-size-fits-all. But collagen isn’t a single compound—it’s a family of proteins.
The Truth:
There are at least 28 types of collagen, but the most important for skin, bones, and joints are Types I, II, and III. Supplements derived from different sources (marine, bovine, chicken) can offer different benefits:
-
Type I & III (bovine or marine) – skin, hair, nails
-
Type II (chicken) – joints and cartilage
✅ Key takeaway: Choosing the right type of collagen matters depending on your goals.
3. Myth: You Get Enough Collagen From Food
Some believe that a good diet provides all the collagen your body needs, making supplements unnecessary.
The Truth:
While bone broth, fish skin, and meat can offer collagen, the natural production of collagen declines sharply with age—especially after 25. Lifestyle factors like smoking, sun exposure, and high sugar intake further reduce collagen levels.
✅ Key takeaway: A balanced diet helps, but supplements can fill the gap—especially as you age.
4. Myth: Collagen Supplements Are Only for Women
There’s a lingering stereotype that collagen is just a beauty product for women. This couldn’t be further from the truth.
The Truth:
Collagen plays a critical role in joint health, muscle recovery, and skin structure—benefits that apply to everyone. In fact, athletes and older adults, regardless of gender, often use collagen to support their physical health.
✅ Key takeaway: Collagen isn’t gendered—it’s essential for human function.
5. Myth: Collagen Supplements Work Instantly
Thanks to flashy ads, some expect collagen supplements to show immediate results—like glowing skin overnight.
The Truth:
Collagen supplementation is a gradual process. Most studies show noticeable results after 8 to 12 weeks of consistent use. Like any wellness habit, consistency is key.
✅ Key takeaway: Real benefits take time. Be patient and consistent.
Bonus Tip: What to Look For in a Collagen Supplement
If you're considering a supplement, make sure it’s:
-
Hydrolyzed (for better absorption)
-
Free from unnecessary fillers or sugar
-
Third-party tested for purity and quality
-
Paired with Vitamin C, which aids collagen synthesis
Final Thoughts
Collagen supplements are often misunderstood, thanks to marketing noise and half-truths. But if we separate fact from fiction, it’s clear they can be a valuable tool for supporting skin, joints, and overall wellness—when used correctly and consistently.
Don’t fall for myths. Instead, rely on evidence-based information to make informed choices about your health.
FAQs About Collagen Supplement Myths
Q: Can I take collagen supplements daily?
A: Yes. Most clinical studies use daily supplementation to measure results effectively.
Q: Are there side effects to collagen supplements?
A: Generally safe, but some may experience mild digestive discomfort. Always consult a healthcare provider if unsure.
Q: Are marine collagen and bovine collagen the same?
A: No. Marine collagen is typically Type I and may be more bioavailable, while bovine collagen often contains Type I and III.










































































![https //g.co/recover for help [1-866-719-1006]](https://newsquo.com/uploads/images/202506/image_430x256_684949454da3e.jpg)


























![[PATREON EXCLUSIVE] The Power of No: How to Say It, Mean It, and Lead with It](https://tpgblog.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/just-say-no.jpg?#)














































![Building A Digital PR Strategy: 10 Essential Steps for Beginners [With Examples]](https://buzzsumo.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/Building-A-Digital-PR-Strategy-10-Essential-Steps-for-Beginners-With-Examples-bblog-masthead.jpg)






