This tiny piece of tech will change how you watch the Indy 500
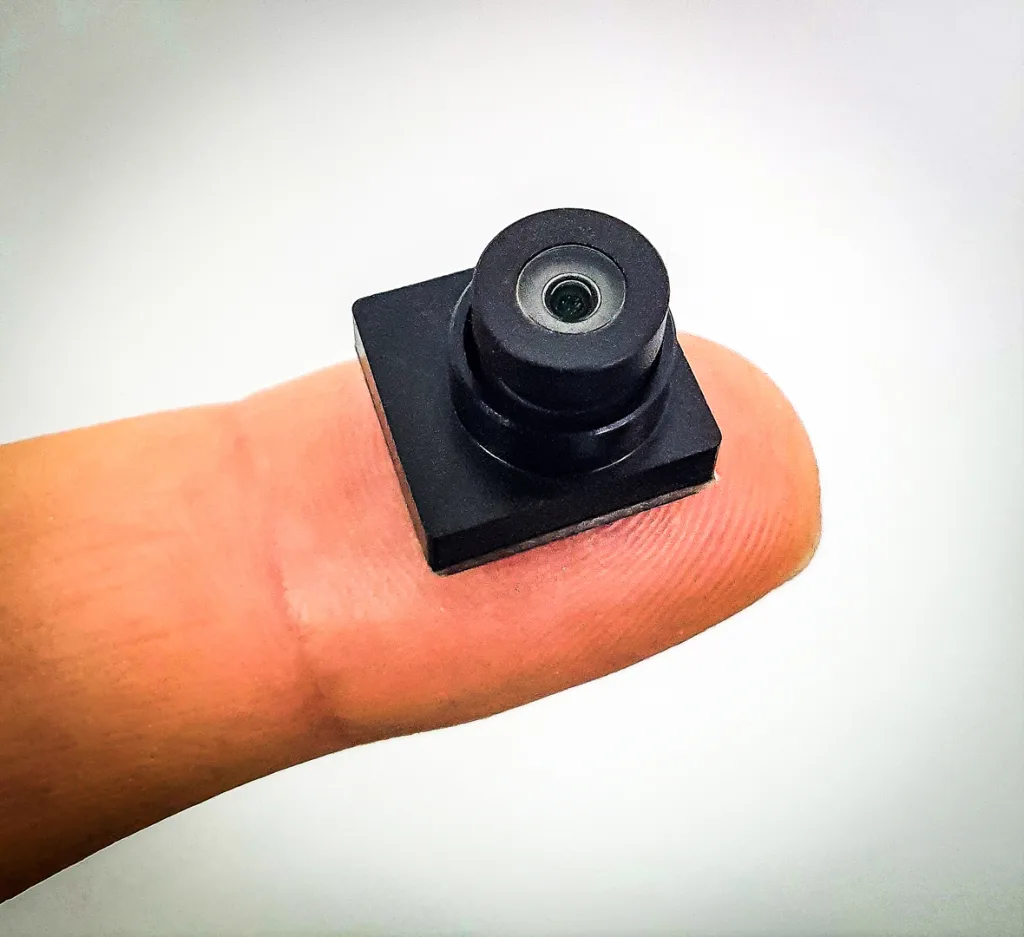
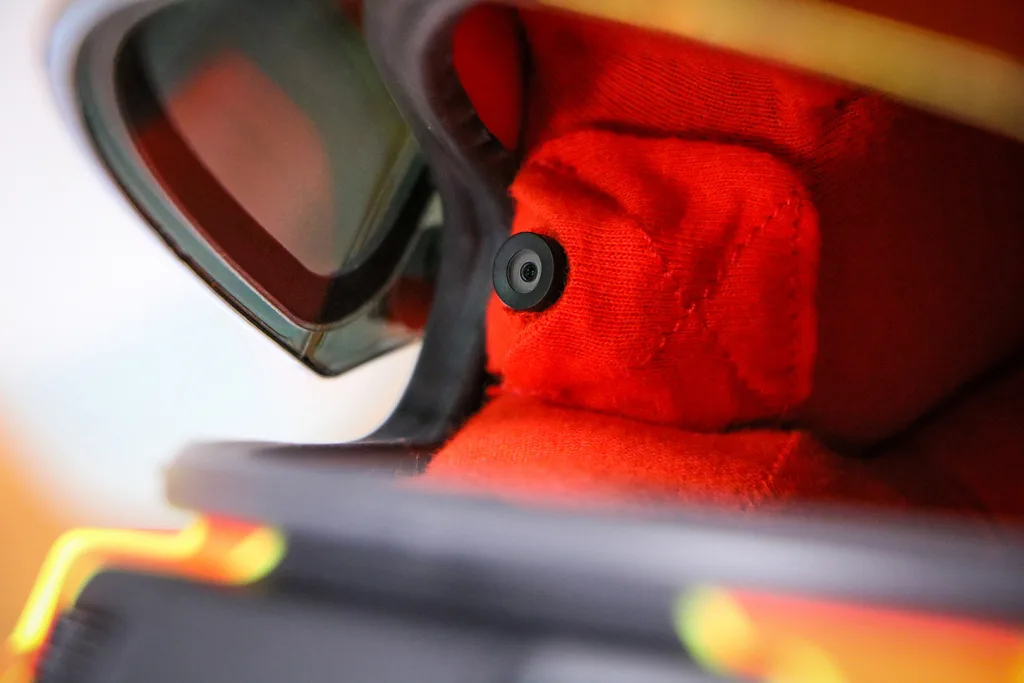
When you describe it in words, the Indianapolis 500 might seem like a boring watch: Cars go round and round an oval track 200 times, totaling 500 miles over the course of a few hours. But if you were a driver, you’d be having a hell of a different experience. Think screaming speeds of 230 miles per hour, pulling 4 Gs on corners, with one’s reflexes and split-second decisions drawing a thin line between victory and tragedy . . . over the course of a few hours. It’s a level of intensity that TV networks have been trying to bring viewers into for years with in-car cameras and things like driver radio communiques. It has been working. Last year, NBC—which covered the spectacle from 2019–2024—netted the most streams of the race ever and averaged 5.34 million total viewers, up from 4.9 million in 2023 and 4.8 million in 2022. This year marks FOX’s first time ever broadcasting it, and they likely want that trend to continue, so they’re throwing all the tech they have at it. And that includes the innovative, diminutive Driver’s Eye, dubbed the world’s smallest live broadcast camera, which brings fans directly into drivers’ helmets (quite literally) like never before. For the first time in Indy 500 history, viewers will have a view of the race exactly as its stars see it from within their helmets—from dramatic passes and vehicle-quaking jousts to the very mechanics of how they operate their cars at such speeds. [Photo: Bell Racing] “Driver’s Eye brings the human factor,” says Alex Miotto Haristos, COO of Racing Force Group, which owns the tech. “It brings the struggle.” And it could bring the ratings, too—especially if it catches on in the series like it has in Formula 1. [Photo: Bell Racing] MORE THAN MEETS THE EYE The UK-born, Italy-raised Haristos is perhaps an unlikely creator of racing gear. He began his career in management consulting and later real estate before acquiring an electronics company and launching it as Zeronoise in 2018 with Stephane Cohen of Bell Racing Helmets. Haristos doesn’t come from a racing background, but rather dubs himself a business engineer who saw it as an opportunity. He says he quickly found himself falling down the rabbit hole into a passion project given the sheer challenging nature of the Driver’s Eye tech, which they began developing in 2019. Ray Harroun driving his Marmon Wasp, the first winner of the Indy Race in 1911. [Photo: Bettmann/Getty Images] That challenge is very real when you’re working on a product meant to be inserted into a race-car driver’s most critical piece of safety gear, particularly in a sport where said driver’s head is sticking out of the car. Racing helmets are modern design marvels that evolved out of leather and cloth versions in the Indy 500’s early days to steel helmets in 1916. According to IndyCar, every driver has a primary and one or two backups, and they’re all custom-fit and produced per FIA (Federation Internationale de l’Automobile) standards. (Want to buy your own? Haristos says that’ll cost you between $5,000 and $8,000.) The outer shell features ultralight carbon fiber; there’s a fireproof liner; a built-in airbag to assist in helmet removal without neck strain; numerous elements to ensure maximum aerodynamics in 200+ mph runs; and audio insulation so drivers can communicate with their teams over the roar of 33 engines on the track. “Your job is to not alter any feature of the helmet,” Haristos says. “The helmet you don’t touch. You have to work with what you have, and you have to manage to integrate everything seamlessly. This is the trick.” [Photo: Bell Racing] The team set out to capture exactly what a driver was seeing on the racetrack, raw and unfiltered, shakes and all—and quickly understood that they couldn’t work on the outer surface of a helmet because it would be a safety issue. So they homed in on the side padding of the helmet that Haristos says is around a centimeter away from the eye, which, given the sensitive proximity, went through the FIA for approval, as well. The organization mandated a minuscule size and weight for the camera, so rather than starting with what image quality they wanted to achieve and so on, “We started working backwards. And in the beginning it was like, No, this is impossible.” Ultimately, the team had to break apart camera design as we know it—a single unit—and separate the internal systems to make it work. They stripped out everything they could for what needed to go in the helmet, and were left with a tiny sensor with the ability to capture high-res video (in the case of the Indy 500, in 1080p, 60fps) in the smallest of real estate. Today, that unit clocks in at 8.8 x 8.8 mm, and weighs less than a dime. Then, they moved the rest of the camera’s guts to the car itself. Which is also a feat, particularly in Indy racing, which involves older cars that are already stuffed to the max from additions over the years. “You can’t do one thing without affecting a
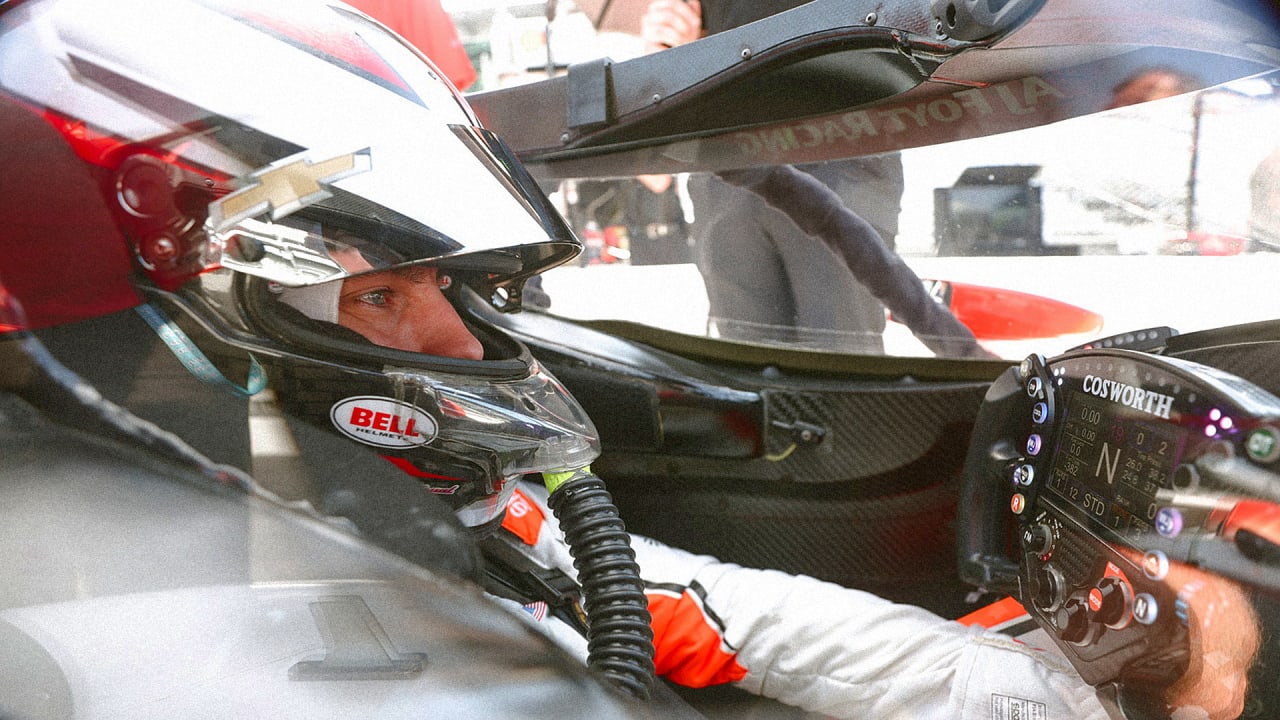

When you describe it in words, the Indianapolis 500 might seem like a boring watch: Cars go round and round an oval track 200 times, totaling 500 miles over the course of a few hours. But if you were a driver, you’d be having a hell of a different experience. Think screaming speeds of 230 miles per hour, pulling 4 Gs on corners, with one’s reflexes and split-second decisions drawing a thin line between victory and tragedy . . . over the course of a few hours.
It’s a level of intensity that TV networks have been trying to bring viewers into for years with in-car cameras and things like driver radio communiques. It has been working. Last year, NBC—which covered the spectacle from 2019–2024—netted the most streams of the race ever and averaged 5.34 million total viewers, up from 4.9 million in 2023 and 4.8 million in 2022. This year marks FOX’s first time ever broadcasting it, and they likely want that trend to continue, so they’re throwing all the tech they have at it. And that includes the innovative, diminutive Driver’s Eye, dubbed the world’s smallest live broadcast camera, which brings fans directly into drivers’ helmets (quite literally) like never before. For the first time in Indy 500 history, viewers will have a view of the race exactly as its stars see it from within their helmets—from dramatic passes and vehicle-quaking jousts to the very mechanics of how they operate their cars at such speeds.

“Driver’s Eye brings the human factor,” says Alex Miotto Haristos, COO of Racing Force Group, which owns the tech. “It brings the struggle.”
And it could bring the ratings, too—especially if it catches on in the series like it has in Formula 1.

MORE THAN MEETS THE EYE
The UK-born, Italy-raised Haristos is perhaps an unlikely creator of racing gear. He began his career in management consulting and later real estate before acquiring an electronics company and launching it as Zeronoise in 2018 with Stephane Cohen of Bell Racing Helmets. Haristos doesn’t come from a racing background, but rather dubs himself a business engineer who saw it as an opportunity. He says he quickly found himself falling down the rabbit hole into a passion project given the sheer challenging nature of the Driver’s Eye tech, which they began developing in 2019.

That challenge is very real when you’re working on a product meant to be inserted into a race-car driver’s most critical piece of safety gear, particularly in a sport where said driver’s head is sticking out of the car. Racing helmets are modern design marvels that evolved out of leather and cloth versions in the Indy 500’s early days to steel helmets in 1916. According to IndyCar, every driver has a primary and one or two backups, and they’re all custom-fit and produced per FIA (Federation Internationale de l’Automobile) standards. (Want to buy your own? Haristos says that’ll cost you between $5,000 and $8,000.) The outer shell features ultralight carbon fiber; there’s a fireproof liner; a built-in airbag to assist in helmet removal without neck strain; numerous elements to ensure maximum aerodynamics in 200+ mph runs; and audio insulation so drivers can communicate with their teams over the roar of 33 engines on the track.
“Your job is to not alter any feature of the helmet,” Haristos says. “The helmet you don’t touch. You have to work with what you have, and you have to manage to integrate everything seamlessly. This is the trick.”

The team set out to capture exactly what a driver was seeing on the racetrack, raw and unfiltered, shakes and all—and quickly understood that they couldn’t work on the outer surface of a helmet because it would be a safety issue. So they homed in on the side padding of the helmet that Haristos says is around a centimeter away from the eye, which, given the sensitive proximity, went through the FIA for approval, as well. The organization mandated a minuscule size and weight for the camera, so rather than starting with what image quality they wanted to achieve and so on, “We started working backwards. And in the beginning it was like, No, this is impossible.”
Ultimately, the team had to break apart camera design as we know it—a single unit—and separate the internal systems to make it work. They stripped out everything they could for what needed to go in the helmet, and were left with a tiny sensor with the ability to capture high-res video (in the case of the Indy 500, in 1080p, 60fps) in the smallest of real estate. Today, that unit clocks in at 8.8 x 8.8 mm, and weighs less than a dime. Then, they moved the rest of the camera’s guts to the car itself. Which is also a feat, particularly in Indy racing, which involves older cars that are already stuffed to the max from additions over the years.
“You can’t do one thing without affecting another,” says Michael Davies, FOX EVP of field and technical management and operations. “There’s no change that you can make on a car that doesn’t fuck something else up. And I’m always reminded of something a very smart man said, which is that when you solve a problem, you inevitably create another one, but you must make sure that the problem you create is smaller than the one that you solved.”
Haristos says that for Indy, they were told that the only available space was on the side of the car by the radiator—not an ideal spot, given the high temperature and so on. So they had to develop a custom housing that was more efficient and could operate at a higher temp while still fitting into the tightest of spaces.
Ultimately, from the helmet camera to the housing, it was crucial that the additions all felt seamless to the driver.
“Comfort in motorsport translates into confidence,” Haristos says. “Confidence translates into performance.”
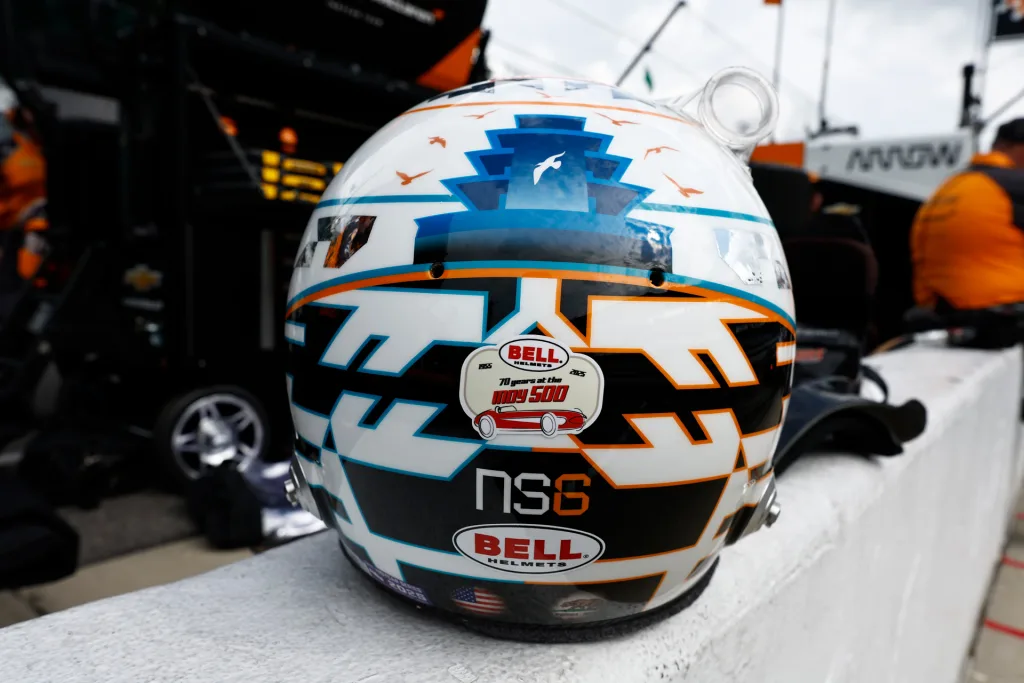

CROSSING THE POND
Safety equipment manufacturer OMP Racing acquired Zeronoise in 2019—and they also acquired Bell, a major purveyor of helmets to Formula 1 and the Indy 500, with 23 of the 33 drivers donning its headwear for the latter. (All the brands would eventually coalesce under the newly formed Racing Force Group in 2021; last year, it did $74.1 million in revenue, up 4.8% from 2023.)
After they developed the first iteration of Driver’s Eye, the team got it into Formula E racing in 2020, and was able to finalize the development of the tech, testing it in Formula 1 in 2021—and giving race fanatics a new, visceral way to experience the sport. It gained ground, and in 2023 became mandatory in Formula 1.
FOX tested Driver’s Eye in some NASCAR races that same year, and now on Sunday you’ll be able to watch the Indy 500 from the perspective of 2023/2024 winner Josef Newgarden, Scott Dixon, Alex Palou, Will Power, Marcus Ericsson and Felix Rosenqvist.
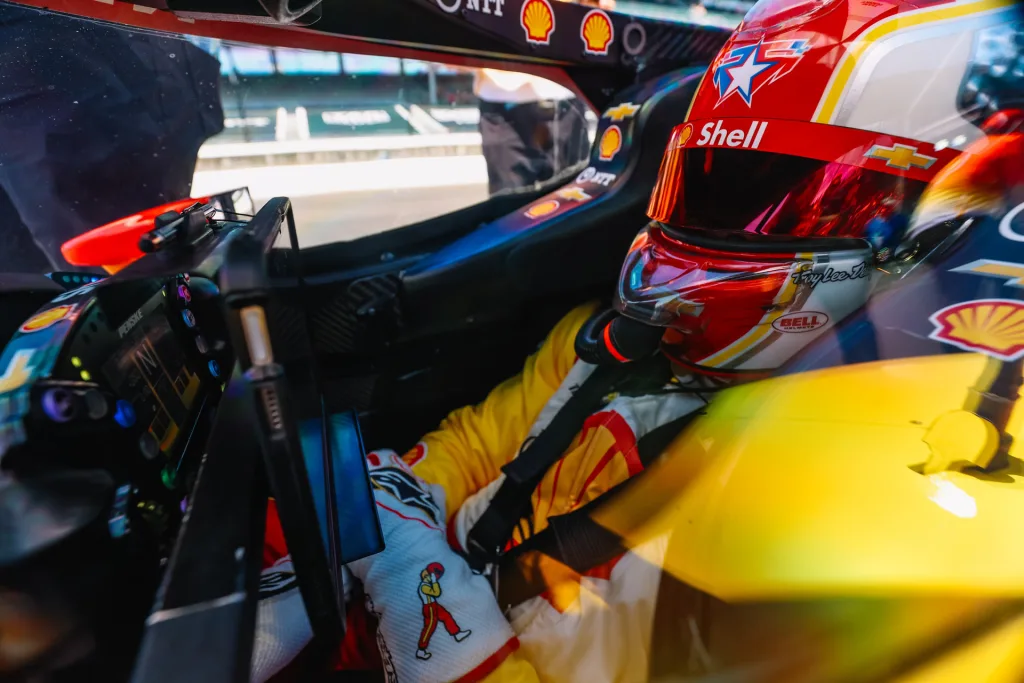

Of course, there’s more tech wizardry at play behind the scenes than merely hooking up a camera. The Driver’s Eye is mounted in a dark helmet with a massive underexposure—and the track is a massive overexposure. Drivers race with different filters and colors on their visors, which they can tear off in layers periodically throughout the race as they get dirty. Moreover, the Indy 500 is hours long, there are varying weather scenarios, the sun and shadows are moving, and everything is very much in a state of flux. Haristos says Driver’s Eye compensates for all of it, from white balance to the varying visor colors, with a mix of automatic and manual controls, making for a seamless sync with the rest of the program. (Which, let’s be honest, is critical—a director has to use the shots, lest Driver’s Eye be rendered obsolete.)
From a production standpoint, FOX’s Davies says that since the system allows for a view of drivers’ hands on the controls and exactly what they’re looking at in any given moment, it’s also a boon to race commentators, who have told him that’s it’s the most useful angle for them in being able to craft a narrative around what’s happening on the track. Moreover, he says the raw nature of the footage truly shows the athleticism at play on the part of the drivers, something that can get lost in traditional shots.
“We can really cover the event from the inside out, instead of the outside in,” he says.
And on top of that, he adds, it’s something sponsors like—and request. Thus a bevy of IndyCar racing’s household names. now driving with the cameras embedded in their helmets.
The Driver’s Eye is just one tiny tool in FOX’s arsenal, which seems designed to shock and awe—and plant a flag in their take on the race. For the first time, live drones will be deployed, including custom high-speed FPV drones; there are more than 100 cameras in play, 108 mics, 16 in-car cameras offering views of drivers’ faces and cockpits, and more (including 5.1 surround sound “that’ll blow your head off”).
“We’re playing some pretty big hits here and looking forward to seeing how it enhances the big race,” Davies says. “You can see it in a completely different way—even if you’ve watched Indy for as long as it’s been on TV.”
























































































![Coaching and Discovery in Product. What High-Performing Teams Are Doing Differently [TPG Live Recap]](https://tpgblog.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/2025-05-08-thumbnail-action.png?#)









![Building A Digital PR Strategy: 10 Essential Steps for Beginners [With Examples]](https://buzzsumo.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/Building-A-Digital-PR-Strategy-10-Essential-Steps-for-Beginners-With-Examples-bblog-masthead.jpg)


















































