How Blown-in Insulation Improves Energy Efficiency in Nevada Homes

Blown-in insulation improves energy efficiency in Nevada homes by sealing gaps and hard-to-reach areas that traditional insulation often misses. This material fills spaces in attics, walls, and floors, creating a continuous thermal barrier that reduces heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. The result is a more stable indoor temperature, less strain on heating and cooling systems, and lower energy bills.
In Nevada’s climate—characterized by intense summer heat, cold winters, and significant temperature swings—effective insulation is essential. Blown-in insulation provides precise coverage, making it especially useful in older homes or those with irregular construction. This article offers a detailed examination of blown-in insulation’s role in energy efficiency, types available, technical specifications, and factors to consider before installation.

How Blown-in Insulation Enhances Energy Efficiency
The effectiveness of blown-in insulation lies in its ability to fill every nook and cranny in a home’s structure. Unlike batt insulation, which comes in fixed sizes and can leave gaps, blown-in material flows into crevices, covering uneven surfaces and awkward angles. This reduces air infiltration—one of the biggest causes of energy loss in homes.
Air leaks allow conditioned air to escape and outside air to enter, forcing HVAC systems to work harder. In Nevada, where cooling demands often dominate energy use, sealing leaks prevents the infiltration of hot air in summer and cold drafts in winter. This lowers energy consumption, reducing cooling and heating costs by up to 20% or more, according to studies on similar climates.
Additionally, blown-in insulation limits thermal bridging. Thermal bridging happens when heat bypasses insulation through framing materials such as studs or joists. Because blown-in insulation fills spaces around these framing components, it cuts down on unwanted heat transfer.
The combination of air sealing and improved thermal resistance makes blown-in insulation a smart energy-saving upgrade for Nevada homes.
Types of Blown-in Insulation and Their Impact
Two primary materials are used in blown-in insulation: cellulose and fiberglass. Each has unique properties that affect energy efficiency, durability, and installation.
Cellulose
Cellulose insulation is made from recycled paper treated with fire retardants. It has a higher density than fiberglass, which allows it to pack tightly and minimize settling over time. Cellulose offers better soundproofing and a higher R-value per inch, typically between 3.2 and 3.8. This higher R-value means better resistance to heat flow, enhancing the thermal envelope of the home.
Because cellulose absorbs moisture moderately, proper moisture control is essential to prevent degradation. When installed correctly in dry environments, it performs well for decades.
Fiberglass
Fiberglass insulation consists of tiny glass fibers that do not absorb moisture, making it naturally mold-resistant. It generally has a lower R-value per inch, ranging from 2.2 to 2.7, but offers excellent fire resistance due to its inorganic composition.
Fiberglass settles less than cellulose, maintaining consistent coverage over time. It is also less dense, which may require greater depth to reach the same R-value.
Material Comparison
|
Feature |
Cellulose |
Fiberglass |
|---|---|---|
|
R-Value per inch |
3.2 – 3.8 |
2.2 – 2.7 |
|
Density |
Higher (packs tightly) |
Lower (fluffier) |
|
Moisture Absorption |
Moderate |
Low |
|
Fire Resistance |
Treated, good |
Naturally high |
|
Settling Over Time |
Moderate |
Low |
|
Soundproofing |
Superior |
Good |
|
Environmental Impact |
High (recycled materials) |
Moderate |
|
Cost |
Moderate |
Lower |
Each option improves energy efficiency, but choosing the right one depends on the home’s construction, moisture levels, and budget.
Technical Data and Performance Metrics
Understanding how blown-in insulation performs involves analyzing key technical factors such as R-value, air permeability, and moisture behavior. These influence how well the material maintains energy efficiency over time.
|
Specification |
Cellulose |
Fiberglass |
|---|---|---|
|
Typical Application Depth |
10 – 14 inches |
12 – 18 inches |
|
Air Permeability |
Low |
Moderate |
|
Thermal Conductivity (k) |
~0.04 W/m·K |
~0.045 W/m·K |
|
Lifespan |
20 – 30 years |
25 – 40 years |
|
Moisture Absorption |
Moderate |
Low |
Both materials offer excellent insulation but their differences affect suitability in Nevada’s arid yet sometimes humid environment. Cellulose’s higher density translates into better air sealing, which is critical for energy savings. Fiberglass’s resistance to moisture and mold makes it preferable in areas prone to humidity or leaks.

The Role of Climate in Insulation Choice for Nevada
Nevada's climate varies significantly between regions but generally includes very hot summers and cold winters with large day-night temperature shifts. This creates specific challenges for home insulation.
Homes in southern Nevada cities like Las Vegas experience extended periods of high temperatures, requiring insulation to prevent heat intrusion. Northern Nevada’s colder winters demand materials that retain heat effectively and prevent drafts.
Blown-in insulation helps maintain a steady indoor temperature in both extremes. It reduces the workload on air conditioners during hot months and helps keep heat inside during cold spells. As reported by the U.S. Energy Information Administration, Nevada households use approximately 50% more energy on cooling than the national average, highlighting the critical need for better insulation.
Effective insulation can reduce cooling and heating energy use by up to 20%, making it a practical investment for residents seeking lower utility bills and improved comfort.
Installation Process and Considerations
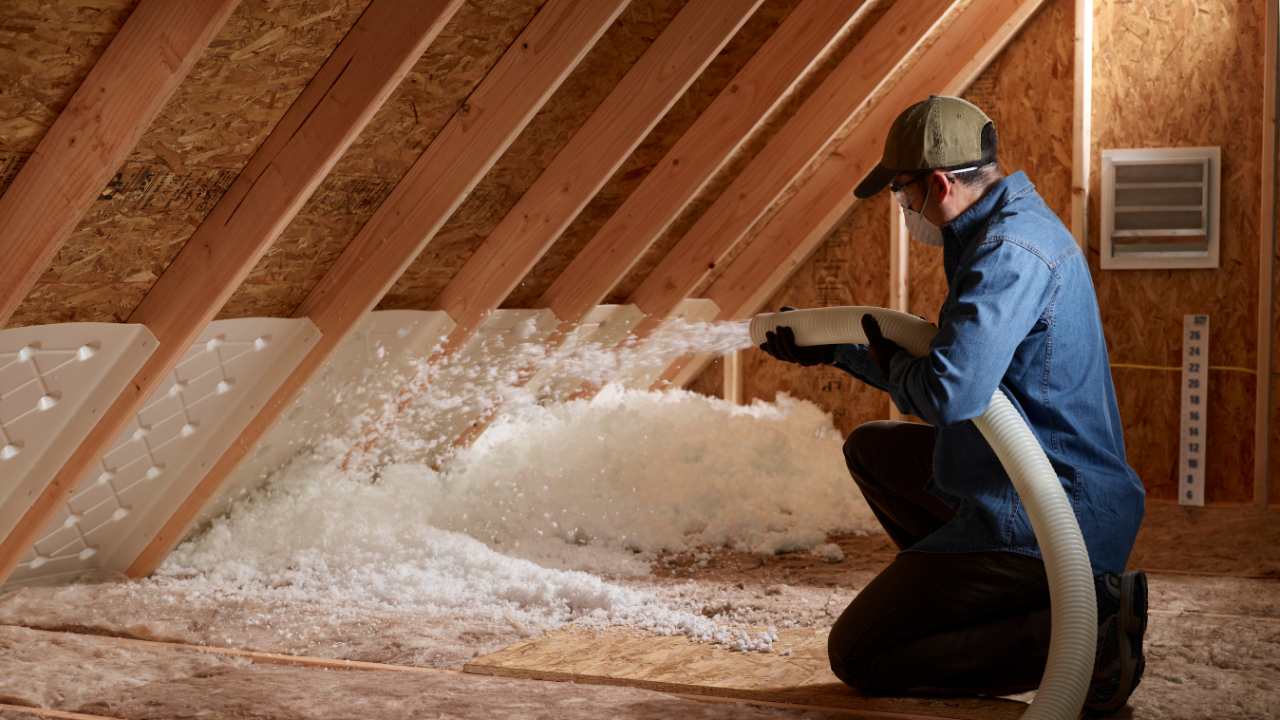
Installing blown-in insulation requires skill and the right equipment. Professional installers use machines to blow loose fibers into spaces, ensuring thorough coverage. The process can be completed in a few hours for most homes, depending on the area treated.
-
Access and Preparation
Access to attics, crawl spaces, or wall cavities is necessary. Walls often require drilling small holes to inject the insulation, which are sealed afterward. Before installation, any leaks in the roofs or plumbing must be fixed to prevent moisture damage to the insulation.
-
Air Sealing
To maximize energy efficiency, installers often combine blown-in insulation with air sealing. Sealing cracks, gaps around windows, doors, and utility penetrations prevents air leaks, further reducing energy loss.
Things to Consider Before Making a Decision
Before committing to blown-in insulation, several factors demand careful evaluation:
-
Current Insulation Condition: If the home already has insulation, blown-in material can be added to improve R-value, but the existing insulation’s condition matters.
-
Moisture Risks: Identify any sources of moisture that could affect the insulation’s performance or longevity.
-
Building Codes: Nevada’s energy codes specify minimum R-values, which vary by region and building type.
-
Budget and ROI: Initial installation costs vary by material and home size, but often pay off in reduced energy bills within a few years.
-
Installation Quality: Proper application is crucial. Poor installation can result in settling, gaps, or moisture problems that undermine benefits.
Considering these points ensures the chosen insulation method delivers maximum energy savings.
Common Questions About Blown-in Insulation
Many homeowners wonder how blown-in insulation compares to alternatives, its longevity, and maintenance.
Blown-in insulation typically lasts 20 to 40 years but requires occasional inspection to check for settling or moisture damage. It can be added over existing insulation to improve performance, making it a common upgrade for older homes.
Properly installed blown-in insulation is safe and complies with fire and health standards. It reduces noise transmission better than batt insulation, contributing to quieter indoor environments.
FAQ
What is the R-value required for Nevada homes? Attics generally require R-38 in cooler regions and R-30 in warmer ones, according to Nevada building codes.
Can blown-in insulation be installed in walls without major renovation? Yes. Installers drill small holes to inject insulation and then seal the holes, making it minimally invasive.
How does blown-in insulation affect indoor air quality? It reduces drafts and dust infiltration, improving air quality. However, moisture control is essential to avoid mold growth.
Is blown-in insulation effective in soundproofing? Yes, cellulose especially offers strong sound-dampening properties.
Will blown-in insulation attract pests? Some cellulose products are treated to deter pests, but insulation alone is not a pest control solution.
Summary
Blown-in insulation enhances energy efficiency in Nevada homes by creating an airtight, well-insulated barrier that controls temperature fluctuations and reduces HVAC load. Its adaptability to fill gaps and irregular spaces outperforms traditional batt insulation, particularly important in Nevada’s demanding climate.
Choosing between cellulose and fiberglass depends on factors such as moisture exposure, soundproofing needs, and budget. Proper installation, combined with air sealing and moisture control, maximizes energy savings and comfort.
Evaluate your home’s specific conditions and local codes before selecting blown-in insulation. A thoughtful choice will improve energy efficiency and provide lasting comfort for decades.
Ready to Achieve Year-Round Energy Efficiency?
Apply these insights now: Schedule a professional evaluation and insulation upgrade to optimize your home’s energy use with Nevada Urethane. Take control of your comfort and reduce your energy bills by installing high-quality blown-in insulation tailored to your home’s needs.
Contact: Nevada Urethane