Ultrasonic Thickness Gauge: A Vital Tool for Accurate Material Assessment
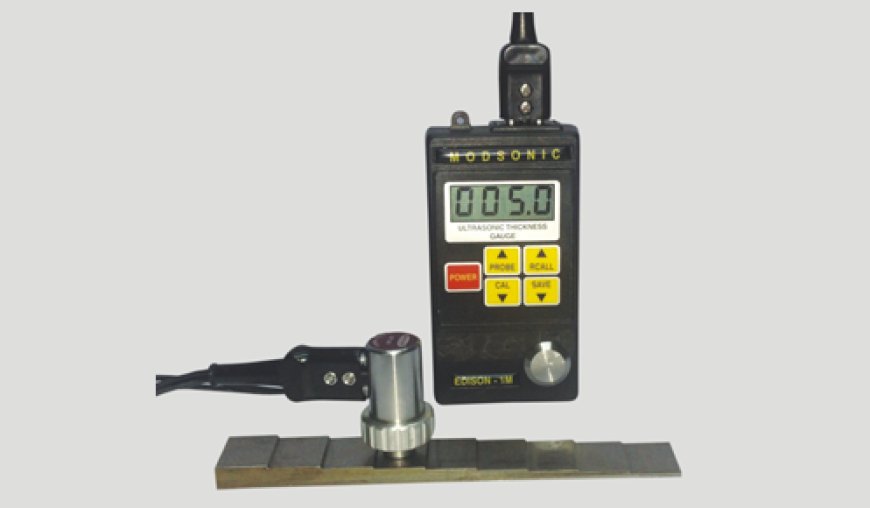

Ensuring the integrity and safety of materials is essential in industries where equipment and infrastructure are exposed to extreme conditions. Whether it’s pipelines carrying hazardous materials, structural components in buildings, or parts in aerospace, the thickness of materials plays a critical role in maintaining safety, performance, and reliability. One of the most effective ways to measure material thickness is through the use of an ultrasonic thickness gauge.
Ultrasonic thickness gauges are essential for providing precise, non-destructive measurements that are crucial for identifying degradation, wear, or corrosion before they result in costly repairs or hazardous failures. In this blog, we will explore how ultrasonic thickness gauges work, their applications in different industries, and why they are indispensable for maintaining the safety and longevity of materials.
What is an Ultrasonic Thickness Gauge?
An ultrasonic thickness gauge is a portable and non-destructive testing (NDT) device used to measure the thickness of materials such as metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites. It works by sending high-frequency sound waves into the material and measuring the time it takes for the waves to reflect off the far side of the material. By calculating the time it takes for the sound waves to travel through the material and return, the device can accurately measure its thickness.
The key advantage of ultrasonic thickness gauges is that they provide non-invasive measurements without causing damage to the material. This feature makes them perfect for industries where materials need to be regularly inspected for degradation or wear without affecting their integrity.
How Does an Ultrasonic Thickness Gauge Work?
The process of using an ultrasonic thickness gauge relies on the speed of sound in the material being tested. Here's how it works in detail:
-
Transducer Emission: The ultrasonic transducer emits high-frequency sound waves into the material.
-
Wave Travel: The sound waves travel through the material until they reach the back surface.
-
Signal Reflection: The sound waves then reflect off the opposite side of the material and return to the transducer.
-
Time Measurement: The device measures the time it took for the sound waves to travel through the material and return.
-
Thickness Calculation: Using the travel time and the known speed of sound in the material, the thickness is calculated.
The ultrasonic thickness gauge then displays the material thickness on a digital screen in real-time, allowing for immediate evaluation of the material’s condition.
Key Components of an Ultrasonic Thickness Gauge:
-
Transducer: This component both emits and receives the ultrasonic sound waves.
-
Couplant: A gel or liquid applied to the surface of the material to ensure the sound waves are transmitted properly.
-
Display Screen: Shows the thickness measurement, typically in units such as millimeters or inches.
-
Power Source: Ultrasonic thickness gauges are usually powered by batteries, making them portable and ideal for on-site testing.
Types of Ultrasonic Thickness Gauges
Ultrasonic thickness gauges are available in several types, each designed for different applications and industry needs. Some of the most common types include:
1. Handheld Ultrasonic Thickness Gauges
Handheld ultrasonic thickness gauges are portable, user-friendly, and designed for quick, on-the-go inspections. These devices are commonly used in industries such as construction, manufacturing, and maintenance. They provide real-time measurements, making them perfect for routine checks on equipment such as pipes, tanks, and other materials.
2. Digital Ultrasonic Thickness Gauges
Digital ultrasonic thickness gauges offer more advanced features, such as data storage, the ability to generate reports, and real-time graphs. These devices are ideal for industries where extensive data tracking is needed, such as aerospace, automotive, and oil and gas. Digital gauges can store historical measurements and produce detailed reports for further analysis.
3. Dual-Element Ultrasonic Thickness Gauges
Dual-element ultrasonic thickness gauges are equipped with two elements in the transducer: one for emitting the sound waves and one for receiving them. This dual-element design enhances the accuracy of the measurements, especially for thicker materials or those with rough surfaces. These gauges are used in high-precision applications such as pressure vessel inspections and aerospace.
4. Coating Thickness Gauges
Coating thickness gauges are designed specifically to measure the thickness of protective coatings on metal surfaces, such as paint, galvanization, or rustproofing. These gauges are widely used in industries like automotive manufacturing, metal fabrication, and construction to ensure coatings are applied correctly to prevent corrosion and extend the lifespan of materials.
Applications of Ultrasonic Thickness Gauges
Ultrasonic thickness gauges have a wide range of applications across multiple industries. Here are some of the key industries that rely on ultrasonic testing:
1. Oil and Gas Industry
The oil and gas industry is heavily dependent on pipelines, tanks, and pressure vessels for transporting and storing hazardous materials. These components are often exposed to extreme environmental conditions, such as corrosive chemicals and high pressures, which can lead to thinning and degradation. Ultrasonic thickness gauges are used to measure the wall thickness of these critical components, detecting corrosion or wear before they lead to leaks, ruptures, or failures. Regular inspections help maintain operational safety and compliance with regulatory standards.
2. Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace industry, where safety is paramount, ultrasonic thickness gauges are used to monitor the integrity of aircraft components, such as wings, fuselages, and engine parts. These components are subject to extreme stresses, and regular inspections with ultrasonic gauges ensure that they meet stringent safety standards. Ultrasonic testing helps detect signs of fatigue, wear, or corrosion that could compromise the safety and performance of the aircraft.
3. Manufacturing and Quality Control
Ultrasonic thickness gauges are essential tools in quality control during manufacturing processes. They help verify that materials, such as metal sheets or pipes, meet thickness specifications and safety standards. Ultrasonic gauges are also used to monitor the quality of welds and joints, ensuring that they are structurally sound. By detecting material defects early, ultrasonic thickness gauges help prevent faulty products from reaching the market, saving time and money on rework.
4. Shipbuilding and Marine Industry
In the shipbuilding and marine industry, ultrasonic thickness gauges are used to monitor the health of vessels exposed to seawater, which accelerates corrosion. Ships, offshore platforms, and other maritime structures are regularly inspected for thinning or corrosion in their hulls, decks, and structural components. Ultrasonic testing helps identify areas that need maintenance, reducing the risk of failure and ensuring the vessel remains safe and seaworthy.
5. Construction and Infrastructure
In construction, ultrasonic thickness gauges are used to inspect structural materials, such as steel reinforcements, beams, and columns. They help detect any areas of corrosion or wear, ensuring the material meets required safety standards. Ultrasonic testing is especially useful in inspecting parts that are difficult to access, such as deep within concrete or metal structures. Regular inspections help prevent structural failure and extend the lifespan of infrastructure.
6. Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, ultrasonic thickness gauges are used to measure the thickness of coatings like rustproofing, paint, and galvanization applied to car parts. Ensuring that coatings are the correct thickness helps protect the metal from corrosion and wear, improving the vehicle's durability and longevity. Ultrasonic testing is also used to inspect the quality of metal parts and welds, ensuring they meet the necessary specifications.
Benefits of Using Ultrasonic Thickness Gauges
Ultrasonic thickness gauges offer a variety of advantages that make them essential tools for industries that require accurate and reliable material testing. Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
One of the primary advantages of ultrasonic thickness gauges is that they provide non-destructive testing. This means the material being tested remains intact, allowing for repeated inspections without damaging the structure or part. This is especially valuable for critical infrastructure, such as pipelines or aircraft components, where any disruption could be costly.
2. High Precision and Accuracy
Ultrasonic thickness gauges offer high accuracy and repeatability. The precise measurements they provide are crucial for detecting even minor variations in material thickness, which could indicate issues such as corrosion or material degradation. By identifying these issues early, ultrasonic testing helps prevent larger, more costly problems.
3. Cost-Effective Maintenance
By detecting wear, corrosion, and material thinning early, ultrasonic thickness gauges help prevent costly repairs or replacements. Routine ultrasonic testing allows companies to plan maintenance activities more effectively, reducing unplanned downtime and expensive emergency repairs. Proactive maintenance helps extend the lifespan of equipment and infrastructure.
4. Portability and Ease of Use
Ultrasonic thickness gauges are lightweight, portable, and easy to use. Many models are handheld, making them ideal for on-site inspections. With minimal training, operators can quickly obtain accurate measurements and assess the condition of the material, ensuring that inspections are fast and efficient.
5. Versatility
Ultrasonic thickness gauges can be used on a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites. They are also suitable for measuring a variety of thicknesses, from thin coatings to thicker materials. This versatility makes ultrasonic gauges applicable across different industries, including automotive, aerospace, oil and gas, and manufacturing.
6. Improved Safety and Compliance
By using ultrasonic thickness gauges, companies can ensure that materials comply with safety standards and regulatory requirements. Regular inspections help detect issues before they result in failures, improving overall safety. Additionally, ultrasonic testing provides documentation that helps companies demonstrate compliance with safety regulations and industry standards.
Conclusion
Ultrasonic thickness gauges are indispensable tools for maintaining the integrity and safety of materials in industries where material strength is critical. Their non-destructive, accurate, and versatile nature makes them ideal for monitoring materials in industries like oil and gas, aerospace, manufacturing, and construction. By providing fast and reliable measurements, ultrasonic thickness gauges help companies detect issues early, reduce maintenance costs, and ensure that equipment remains safe and reliable.
Whether used for checking the corrosion of pipelines, inspecting the quality of coatings on automotive parts, or ensuring the safety of structural components in construction, ultrasonic thickness gauges are essential for ensuring material durability and operational efficiency. Regular use of these gauges can extend the lifespan of critical infrastructure, improve safety, and reduce the risk of unplanned downtime, making them a valuable investment for industries worldwide. Keep Writting




































































![https //g.co/recover for help [1-866-719-1006]](https://newsquo.com/uploads/images/202506/image_430x256_684949454da3e.jpg)


























![[PATREON EXCLUSIVE] The Power of No: How to Say It, Mean It, and Lead with It](https://tpgblog.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/just-say-no.jpg?#)



















































