Field Management Systems: Tools for Smarter Farming
A field management system is a digital platform designed to help farmers monitor, manage, and optimize their field operations.
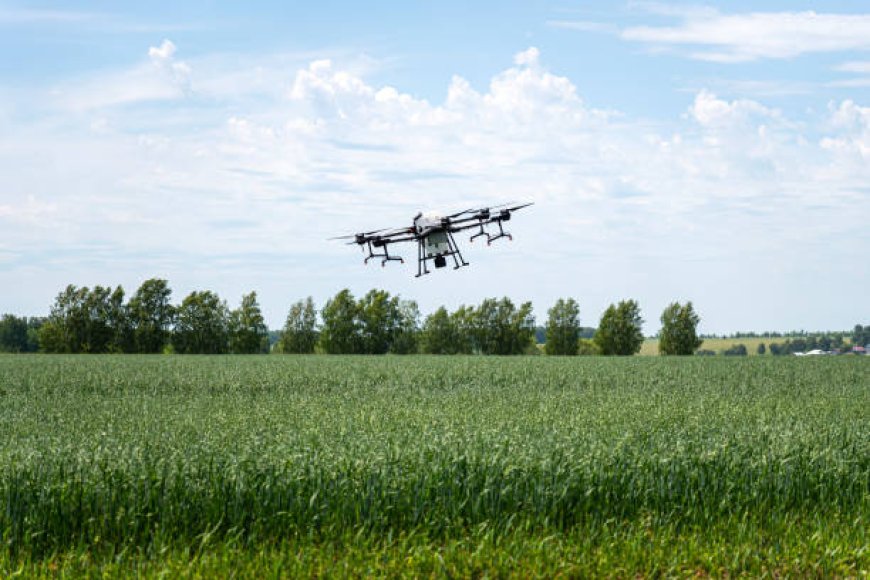

In today’s fast-evolving agricultural landscape, technology is transforming the way farmers manage their land, crops, and resources. A field management system has emerged as one of the most powerful tools for modernizing farming practices. These systems integrate data collection, analysis, and decision-making tools to help farmers improve efficiency, boost yields, and reduce environmental impact. As global food demand rises and sustainability becomes more critical, the adoption of field management systems is no longer a luxury—it's a necessity.
What is a Field Management System?
A field management system is a digital platform designed to help farmers monitor, manage, and optimize their field operations. It combines real-time data from various sources—such as satellite imagery, weather stations, soil sensors, and machinery—with software tools that assist in planning and executing farming activities. From seed selection and planting schedules to irrigation, pest control, and harvest planning, a field management system offers end-to-end support for informed decision-making.
These systems are often cloud-based, allowing access from anywhere using computers, tablets, or smartphones. They are customizable based on the size of the farm, the type of crops grown, and the specific challenges faced by the farmer.
Key Features of a Field Management System
-
Field Mapping and GPS Integration
One of the core features of a field management system is field mapping using GPS technology. This allows farmers to create detailed maps of their plots, track machinery movement, and analyze crop performance by zone. Field mapping supports precision agriculture, where inputs like water and fertilizers are applied only where needed.
-
Weather Monitoring and Forecasting
Integrating local weather data helps farmers make timely decisions. A field management system can alert users to upcoming weather events, such as rainfall or frost, so they can adjust irrigation schedules, apply protective measures, or delay harvesting.
-
Soil Health and Nutrient Management
Many systems include tools for soil testing and nutrient tracking. By understanding soil conditions across different fields, farmers can apply fertilizers more effectively, avoiding overuse and reducing costs.
-
Crop Monitoring and Health Tracking
Satellite imagery and drone data allow for remote monitoring of crop health. The system can detect signs of disease, pest infestation, or water stress early, enabling quick interventions. This proactive approach reduces crop loss and supports sustainable practices.
-
Task Planning and Record Keeping
A field management system helps in planning daily activities, assigning tasks to workers, and keeping detailed records of all operations. This simplifies compliance with regulatory standards and helps track performance over time.
-
Input and Cost Management
By tracking input usage such as seeds, pesticides, and fuel, the system helps manage farm budgets and improve profitability. Farmers can analyze which practices yield the best results and reduce wasteful spending.
Benefits of Using a Field Management System
-
Improved Efficiency
Automation and centralized data access save time and reduce manual errors. With better coordination between field operations, farmers can manage larger areas with fewer resources.
-
Higher Yields
By making data-driven decisions, farmers can optimize growing conditions for each crop. Timely application of water and nutrients, along with early detection of problems, leads to healthier crops and better yields.
-
Sustainability
A field management system promotes sustainable agriculture by reducing the overuse of water, chemicals, and fuel. It encourages responsible land use and protects long-term soil health.
-
Better Risk Management
The system helps farmers respond quickly to unpredictable events like droughts, pests, or market price fluctuations. Access to accurate and timely data allows for faster and smarter decisions during crises.
-
Regulatory Compliance
Governments and buyers increasingly require documentation on farming practices. A field management system simplifies reporting and ensures compliance with environmental and food safety standards.
Adoption Challenges
Despite the clear benefits, there are challenges to adopting a field management system:
-
Cost: Initial setup and subscription fees may be a barrier for small-scale farmers.
-
Technical Knowledge: Farmers may need training to use the system effectively.
-
Connectivity Issues: In remote rural areas, poor internet access can hinder system performance.
To overcome these issues, governments and agricultural extension services are beginning to offer subsidies, training programs, and infrastructure support to promote adoption.
Future Trends
The future of the field management system is closely tied to advances in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT). Future systems will likely offer predictive analytics, autonomous equipment integration, and even more precise environmental modeling.
-
AI Integration: Predictive tools will help forecast yields, detect patterns in pest behavior, and suggest optimal planting strategies.
-
IoT Devices: Smart sensors in the field will continuously feed real-time data to the system, enabling even more accurate monitoring and control.
-
Mobile-First Platforms: User-friendly mobile apps will expand accessibility, even for small and mid-sized farms in developing countries.
Conclusion
A field management system is a transformative tool that supports smarter, more sustainable farming. By integrating technology into everyday agricultural practices, farmers can boost productivity, reduce environmental impact, and enhance profitability. As the world faces increasing pressure to feed a growing population while preserving natural resources, adopting such systems will be crucial to the future of agriculture. Whether for a large commercial operation or a small family farm, embracing a field management system is a step toward a more efficient and resilient agricultural future.
































































![https //g.co/recover for help [1-866-719-1006]](https://newsquo.com/uploads/images/202506/image_430x256_684949454da3e.jpg)