Thermal Resistance Advantages of Closed-Cell Foam in Leander, Tx
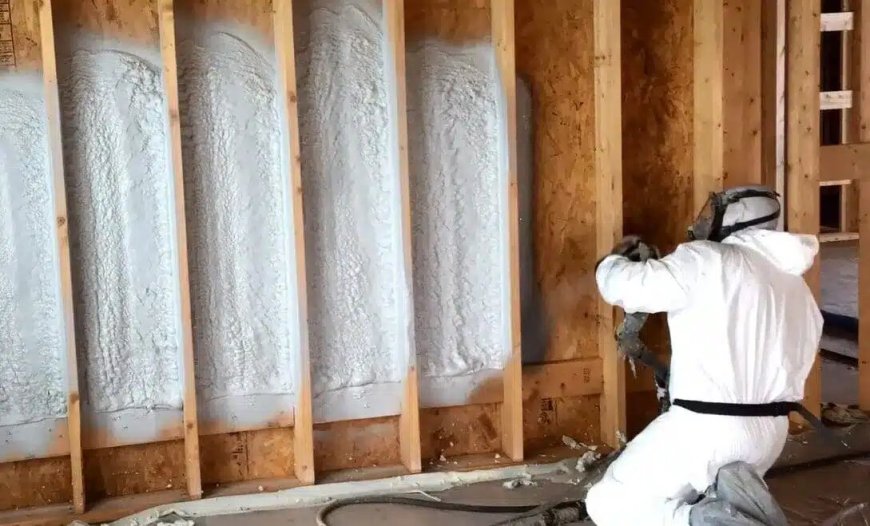

Closed-cell foam provides one of the most effective thermal barriers available for homes and buildings. In Leander, TX, where high summer temperatures and humidity levels persist for much of the year, this type of insulation plays a direct role in controlling indoor temperature and reducing energy usage. Its high R-value per inch, moisture resistance, and rigidity set it apart from traditional insulation options.
Closed-cell spray foam resists heat flow more effectively than other materials. This reduces air conditioning demands, prevents moisture infiltration, and strengthens structural elements when properly installed. For property owners in Leander and surrounding areas, this material supports long-term thermal stability in both residential and commercial environments. This article explores the advantages of closed-cell foam in Leander, TX, including its technical characteristics, performance comparisons, key installation considerations, and frequently asked questions—particularly those related to its superior thermal resistance.
Thermal Resistance Compared to Other Insulation Types
Closed-cell foam achieves high thermal resistance because of its dense structure and sealed air pockets. This structure blocks heat transfer and also limits air movement, which lowers the risk of thermal bridging and energy loss through framing. Traditional insulation like fiberglass or cellulose leaves gaps and seams where air can escape. Closed-cell foam creates a tight seal that supports better energy retention.
Comparison Table: R-Value per Inch and Key Performance Attributes
|
Insulation Type |
R-Value per Inch |
Air Barrier |
Water Resistance |
Structural Support |
|
Closed-Cell Foam |
6.5–7.0 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Open-Cell Foam |
3.5–3.7 |
Yes |
No |
No |
|
Fiberglass Batts |
2.9–3.8 |
No |
No |
No |
|
Cellulose |
3.2–3.8 |
No |
No |
No |
|
Rigid Foam Board |
4.5–5.0 |
Varies |
Varies |
Moderate |
Closed-cell foam provides nearly twice the R-value per inch compared to open-cell foam and significantly more than fiberglass batts. This makes it ideal in areas where space is limited, such as wall cavities or vaulted ceilings. Its water-resistant properties make it well-suited for crawlspaces and basements, which are prone to moisture issues in humid Texas climates.
Technical Specifications and Performance Data
To understand why closed-cell foam performs better than most alternatives, it helps to examine the technical specifications that affect thermal performance and durability. The foam is made of polyurethane and expands when sprayed, forming a solid structure with a closed-cell composition. This means more than 90% of the cells remain intact and closed, preventing air and moisture infiltration.
Technical Data Table
|
Property |
Specification |
|
R-Value per Inch |
6.5–7.0 |
|
Density |
1.75–2.25 lb/ft³ |
|
Air Permeability |
< 0.02 L/s•m² @ 75 Pa |
|
Water Absorption |
< 0.3% by volume |
|
Vapor Permeance (1 inch) |
0.8–1.2 perms |
|
Application Temperature |
45°F to 120°F |
|
Service Temperature Range |
-40°F to 180°F |
|
Closed Cell Content |
> 90% |
|
Fire Rating |
Class I (ASTM E84) |
These specifications show the foam’s ability to maintain insulation performance under a range of temperatures and humidity levels. In climates like Leander’s, where cooling loads are high for extended months, a higher R-value with low permeability is critical. Homes using closed-cell insulation experience fewer indoor temperature fluctuations and lower monthly cooling costs.
Closed-cell foam meets Class I fire resistance standards and supports compliance with Texas building codes when applied properly. A professional application is necessary to ensure performance characteristics are met, especially regarding thickness and curing conditions.
Closed-Cell Foam in the Central Texas Climate
Leander faces extended periods of high heat, often surpassing 100°F in summer. With humidity from the Gulf adding to the challenge, maintaining consistent indoor comfort can strain older or poorly insulated buildings. Closed-cell foam provides a long-lasting, multi-function insulation layer that adapts well to both heat and moisture.
It also improves energy efficiency by closing gaps in building envelopes. Unlike traditional insulation that compresses over time or shifts in wall cavities, closed-cell foam bonds directly to surfaces. This includes metal, wood, and concrete, all common in Central Texas construction.
Property owners in Leander who upgrade to closed-cell foam often report:
-
More stable indoor temperatures
-
Reduced HVAC run times
-
Improved comfort in attics and crawlspaces
-
Lower energy bills across summer and winter months
Market Data Insight
Energy Star reports that sealing and insulating attics can save up to 15% on heating and cooling costs. In Texas, where cooling often dominates energy use, some homeowners have reported 20–30% savings after replacing traditional insulation with closed-cell foam.
Bonus Tip: Installing closed-cell foam in unvented attic assemblies improves energy control and can extend HVAC system lifespan by reducing workload.
Considerations Before Choosing Closed-Cell Foam
Choosing insulation involves more than just comparing R-values. Closed-cell foam performs well under a wide range of conditions, but the decision to use it depends on several local and structural factors. These include wall assembly types, moisture levels, access for application, and long-term goals for energy efficiency.
Key Factors to Evaluate
1. Area of Application
Closed-cell foam works best in enclosed or semi-enclosed areas where both insulation and moisture resistance are needed. Good examples include attics, crawlspaces, rim joists, and wall cavities. Open or vented spaces may need additional sealing.
2. Installation Access and Depth
Proper installation requires clear access to surfaces. In retrofit situations, tight spaces or obstructions may limit the installer’s ability to reach all areas. Foam thickness must also be managed—typically two inches for walls and up to three inches for attics.
3. Building Code and Fire Barrier Compliance
In many cases, building code requires closed-cell foam to be covered by a 15-minute thermal barrier, such as drywall. Some applications require an ignition barrier as well. Professional contractors will guide this part of the process.
4. Cost Considerations
While closed-cell foam has a higher initial cost than fiberglass or open-cell alternatives, it lasts longer and reduces long-term energy usage. Homeowners should evaluate initial investment against expected energy savings and durability.
Bonus Tip: For multi-story homes, insulating between floors with closed-cell foam can help reduce noise transmission and improve conditioned air separation.
Questions Often Asked About Closed-Cell Foam
Does closed-cell foam degrade over time?
Not under normal conditions. It maintains structure and performance for decades if installed correctly.
Can it be sprayed in winter?
Yes, but temperature and humidity must be controlled. Most products apply effectively between 45°F and 120°F.
Does closed-cell foam absorb water in floods?
No. It resists water infiltration, unlike fiberglass, which becomes saturated and loses effectiveness.
Is it compatible with HVAC ducts and wiring?
Yes. It can be applied around ducts and wiring safely, but licensed professionals should handle application to avoid blocking airflow or creating fire hazards.
What’s the typical lifespan?
50+ years with no need for replacement under standard conditions.
FAQ
How thick should closed-cell foam be in walls in Leander, TX?
Typically, 2 inches meets code and provides R-13 to R-14 insulation.
Is it safe for homes with children or pets?
Yes, once cured. Off-gassing only occurs during installation, and proper ventilation avoids any exposure risks.
Can closed-cell foam reduce noise?
It offers some sound dampening, though not as much as open-cell foam. Its primary benefits are thermal and moisture resistance.
Does it increase home resale value?
Yes. Homes with higher insulation performance appeal to buyers due to lower utility costs and improved comfort.
Can it be applied over old insulation?
In some cases. It depends on the condition and material of the existing insulation. Removal may be recommended for optimal bonding.
Summary of Key Points
Closed-cell foam insulation provides strong thermal resistance, moisture control, and long-term durability, especially useful in the high-heat environment of Leander, TX. With an R-value of 6.5–7.0 per inch, it outperforms most insulation materials in energy retention and sealing performance. It’s suitable for wall cavities, attics, crawlspaces, and other areas where energy efficiency is a priority. Homeowners should assess area coverage, installation logistics, and code compliance before choosing this material. While the initial cost is higher, the long-term energy savings, durability, and added structural support provide a strong return on investment.
Ready to Achieve Energy Efficiency in Every Season?
Apply these insights now: Schedule your insulation assessment with Spray Foam Tech and explore closed-cell solutions built for Texas heat.
Contact
Spray Foam Tech