Why Roof Coatings Are Essential for Long-Term Roof Health
This article delivers a full breakdown of professional roof coating contractor, how they function, and what factors to evaluate before application.
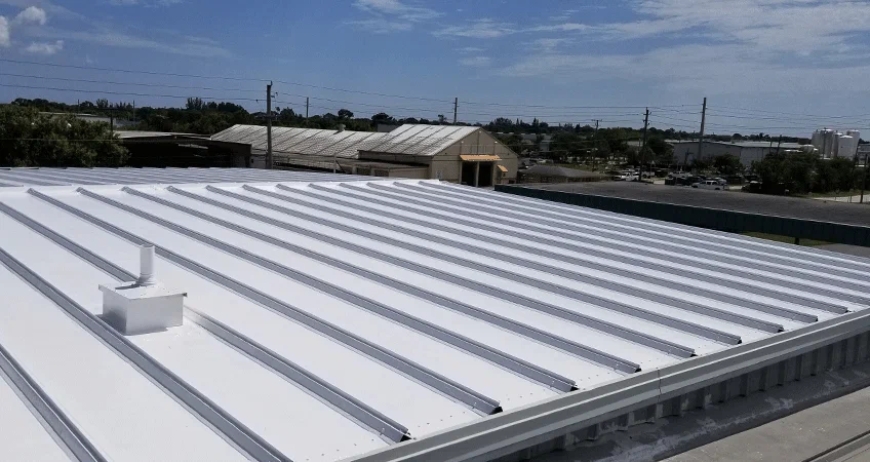

Roof coatings are essential for long-term roof health because they significantly extend a roof’s lifespan, increase its resistance to environmental damage, and improve building energy efficiency. They form a durable, protective membrane that shields roofing materials from UV radiation, thermal expansion, and water infiltration—key contributors to premature roof failure. Without coatings, roofs are more likely to degrade quickly, leading to frequent repairs, costly replacements, and higher utility bills.
This article delivers a full breakdown of professional roof coating contractor, how they function, and what factors to evaluate before application. It’s built to help building owners, facility managers, and contractors understand how to make informed decisions—backed by data, not hype.
Benefits of Roof Coatings
Roof coatings go beyond surface aesthetics. They act as a functional layer of protection that reinforces a roof’s structural performance while providing measurable energy savings.
Primary Benefits
-
Extended Roof Life
Roof coatings add an average of 10 to 20 years to the life of an existing roof system. This extended service reduces waste and delays the high cost of full roof replacement.
-
Waterproofing and Leak Prevention
Coatings create a monolithic membrane that fills cracks and seals joints, preventing water infiltration. This is especially useful on older roofs showing signs of wear but still structurally sound.
-
Reflectivity and Energy Efficiency
Reflective coatings like white acrylics and silicones deflect sunlight, which keeps roof temperatures lower. In warm climates, this can reduce cooling energy consumption by up to 30%.
-
Reduced Maintenance Costs
Coated roofs require fewer repairs and less frequent inspections. Routine maintenance becomes more predictable, minimizing emergency service calls.
-
Environmental Impact
Applying a coating instead of replacing a roof helps reduce landfill waste. Some coatings are low in VOCs and contribute to LEED credits or green building goals.
Comparison of Roof Coating Types
Different coating types serve different needs. Each material has unique strengths based on its chemistry and performance characteristics. Understanding their differences helps match the right coating to your roof’s demands.
|
Type |
Base Material |
Best Use Case |
Durability |
UV Resistance |
Waterproofing |
Cost ($/sq.ft) |
|
Acrylic |
Water-based |
Mild climates, UV protection |
Moderate |
High |
Moderate |
0.75–1.50 |
|
Silicone |
Solvent-based |
Wet climates, ponding areas |
High |
Very High |
Very High |
1.50–3.00 |
|
Polyurethane |
Solvent-based |
High traffic, hail zones |
Very High |
High |
High |
2.00–4.00 |
|
Asphalt Emulsion |
Bitumen-based |
Industrial, basic sealing |
Low |
Low |
High |
0.50–1.00 |
Bonus Tip: For roofs with frequent foot traffic or exposure to mechanical equipment, polyurethane coatings offer the best durability and impact resistance.
Technical Specifications
Choosing a coating requires more than knowing the price and material. Review technical data to determine performance under real-world conditions.
|
Property |
Standard Acrylic |
Silicone |
Polyurethane |
|
Elongation (%) |
250–300 |
150–250 |
200–400 |
|
Tensile Strength (psi) |
250–400 |
200–500 |
300–900 |
|
Reflectivity (%) |
80–90 |
85–95 |
70–85 |
|
Dry Film Thickness (mil) |
10–20 |
20–30 |
15–25 |
|
Service Life (yrs) |
10–15 |
15–20 |
15–25 |
Things to Consider Before Making a Decision
Before applying any roof coating, evaluate critical factors that affect performance, cost, and long-term outcomes. Coatings aren’t universal solutions—they must match roof conditions, climate, and structural needs.
1. Condition of the Existing Roof
-
Coatings are most effective on roofs that are weathered but still functional
-
Extensive cracks, rust, or saturated insulation require repairs before coating
2. Climate and Weather Patterns
-
Rain-prone areas: Silicone performs better under standing water conditions
-
Hot, sunny climates: Acrylic reflects sunlight effectively and reduces heat absorption
3. Roof Slope and Drainage
-
Flat roofs need coatings with strong waterproofing to handle ponding
-
Sloped roofs can use more reflective or flexible materials for expansion and contraction
4. Surface Preparation Needs
-
Old coatings, dust, and oil must be cleaned off to ensure adhesion
-
Power washing or primer application may be necessary
5. VOC Regulations and Compliance
-
Some solvent-based coatings have higher VOCs and may be restricted by local codes
-
Always check material safety data sheets (MSDS) for compliance
Bonus Tip: Conduct a field adhesion test before full application. This helps verify that the coating will bond properly to the existing surface.
Application Process Overview
Understanding the steps involved in coating a roof helps estimate time, cost, and preparation requirements.
General Steps
-
Inspection and Surface Evaluation
Identify existing damage and confirm the roof’s suitability for coating.
-
Cleaning
Pressure washing or mechanical cleaning removes dirt and debris.
-
Repairs and Priming
Apply sealants, fabric reinforcement, or primers as needed.
-
Coating Application
Use spray, roller, or brush depending on the material and substrate.
-
Cure Time
Coatings generally dry within 24–48 hours, weather permitting.
Market Data Snapshot
The U.S. commercial roof coating market grew to over $1.3 billion in 2023, with demand rising due to aging infrastructure and green building mandates. Reflective “cool roof” coatings are now standard in many municipalities, especially in the Southwest and Southeast U.S. where cooling efficiency is a priority.
Maintenance After Coating
A roof coating isn’t a set-it-and-forget-it solution. Proper maintenance ensures it reaches its full lifespan.
Maintenance Guidelines
-
Annual Inspections: Look for peeling, blisters, or impact damage
-
Cleaning: Remove dirt buildup and biological growth with mild detergents
-
Re-Coating: Many systems allow for re-application every 10–15 years without full removal
Bonus Tip: Document each inspection and maintenance step. Keeping a coating history improves warranty claims and future planning.
Why Roof Coatings Are Essential for Long-Term Roof Health FAQ
What roofs can be coated?
Flat and low-slope roofs are the most common candidates. Suitable materials include EPDM, TPO, modified bitumen, and metal roofs.
What’s the difference between re-roofing and coating?
Re-roofing replaces the roof entirely. Coating enhances and preserves the current roof without removing materials.
How long do coatings last?
Depending on the material and environmental conditions, coatings typically last between 10 and 25 years.
Are coatings environmentally friendly?
Yes. Many coatings are low-VOC and reflect sunlight, reducing cooling energy use and emissions.
Can I apply the coating myself?
Small residential roofs may be DIY-friendly, but commercial systems should always be installed by trained professionals.
Make the Right Decision
Choosing to coat a roof is a proactive step toward long-term building protection. The right coating system reduces costs, delays replacement, and improves energy performance. Success depends on careful evaluation of existing conditions, appropriate material selection, and proper application techniques. Take the time to assess your roof, match it to a proven coating solution, and follow manufacturer guidelines.
A well-chosen and expert insulation service can provide decades of performance, making it one of the most cost-effective decisions for long-term roof health.
Reviewer:
Maria Lopez offered detailed feedback after reviewing this post. Her 10 years of experience in spray foam work helped guide the tone and suggestions toward realistic strategies.