Best Practices for Earthing Testing in Solar Farm Services and Power System Analysis
Earthing testing is a critical component in ensuring electrical safety and system reliability across a variety of power infrastructure projects, especially in solar farm services and power system analysis.
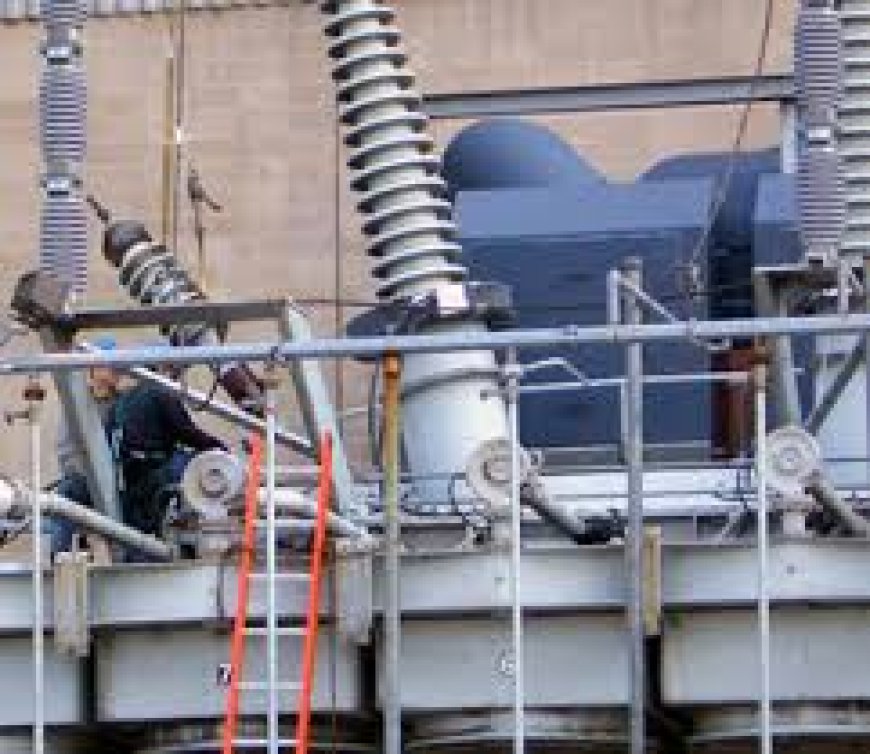

Earthing testing is a critical component in ensuring electrical safety and system reliability across a variety of power infrastructure projects, especially in solar farm services and power system analysis. Accurate earthing testing methods for electrical safety are essential to protect personnel, equipment, and ensure compliance with safety standards. This article explores the key earthing testing techniques and best practices applied during substation design, testing & commissioning, high voltage O&M, solar farm services, power system analysis, high voltage testing, protection & control, and 3D digital substation designs.
Soil Resistivity Earthing Testing for Industrial Installations
A foundational step in designing any earthing system is soil resistivity earthing testing for industrial installations. Soil resistivity determines how well the earth can conduct electrical currents, directly affecting the grounding system’s performance. The Wenner four-pole method is widely used, involving four electrodes placed at equal distances to inject current and measure voltage drop. This method provides accurate soil resistivity data, which is crucial for designing effective grounding grids in substations and solar farms, ensuring fault currents dissipate safely.
Fall-of-Potential Earthing Testing Procedure Explained
The fall-of-potential earthing testing procedure explained involves placing three electrodes: the earth electrode under test, a current electrode, and a potential electrode. By injecting a known current and measuring the voltage drop, the earth resistance is calculated. This method is the industry standard during testing & commissioning and routine high voltage O&M, verifying that grounding systems meet design specifications and safety regulations.
Selective Earth Ground Testing with Clamp Meters
In complex grounding networks, selective earth ground testing with clamp meters allows technicians to measure the resistance of individual grounding conductors without disconnecting them. This non-intrusive method is invaluable during troubleshooting grounding system faults using earthing testing, enabling quick identification of high-resistance points and reducing system downtime.
How to Perform Stakeless Earthing Testing Effectively
How to perform stakeless earthing testing effectively is important in environments where driving auxiliary electrodes is impractical, such as congested urban substations or industrial plants. This method uses clamp-on instruments to induce a high-frequency signal through the grounding loop and measure resistance without the need for additional stakes. Ensuring a complete grounding loop and following manufacturer guidelines carefully are key to obtaining accurate results.
Earthing Testing for Low-Resistance Grounding Systems
Earthing testing for low-resistance grounding systems is critical to ensure rapid fault current dissipation and personnel safety in high voltage substations. Precise measurement techniques, often combining fall-of-potential and selective clamp methods, verify that resistance values remain within safe limits, preventing hazardous touch and step voltages.
Step-by-Step Guide to Earth Resistance Testing with Stakes
A step-by-step guide to earth resistance testing with stakes includes selecting appropriate locations for current and potential electrodes, driving stakes into the ground at specified distances, connecting the earth tester, injecting current, measuring voltage drop, and calculating resistance. Multiple measurements at different distances help plot resistance curves. This procedure is standard during substation commissioning and preventive maintenance to verify grounding effectiveness.
Portable Earthing Testing Devices for Field Engineers
Portable earthing testing devices for field engineers enable quick and accurate on-site measurements of earth resistance and soil resistivity. These compact, battery-operated instruments comply with ASTM standard compliant earthing testing techniques, ensuring reliable results for solar farm services, textile mills, factories, and other industrial applications.
Earthing Testing and Soil Resistivity Measurement Best Practices
Best practices for earthing testing and soil resistivity measurement include conducting tests under stable soil moisture conditions, using calibrated equipment, and following standardized procedures such as fall-of-potential and Wenner four-pole methods. Proper documentation and interpretation of results are essential for designing safe and effective grounding systems.
Electrical Earthing Testing for Textile Mills and Factories
Electrical earthing testing for textile mills and factories is vital due to the high electrical loads and sensitive equipment involved. Reliable grounding prevents electrical shocks, equipment damage, and production downtime, ensuring worker safety and operational continuity.
Troubleshooting Grounding System Faults Using Earthing Testing
Troubleshooting grounding system faults using earthing testing involves identifying issues such as corrosion, loose connections, or increased resistance joints. Selective earth ground testing with clamp meters or fall-of-potential methods helps pinpoint faults early, allowing timely corrective action and minimizing operational disruptions.
Comprehensive Earthing Testing for Renewable Energy Systems
Renewable energy systems, particularly solar farms, require comprehensive earthing testing for renewable energy systems to maintain safety and performance. Regular soil resistivity and earth resistance measurements help ensure grounding grids function correctly despite environmental challenges, protecting personnel and equipment.
Benefits of Selective Earth Ground Testing in Complex Installations
Benefits of selective earth ground testing in complex installations include the ability to isolate and test individual grounding points without system disruption. This targeted approach improves maintenance efficiency and reduces downtime in substations and industrial plants.
Earthing Testing Using Fall-of-Potential and Wenner Four-Pole Methods
Combining earthing testing using fall-of-potential and Wenner four-pole methods provides a thorough evaluation of grounding systems. While fall-of-potential measures earth resistance, the Wenner method assesses soil resistivity. Together, they provide comprehensive data critical for substation design, testing & commissioning, and ongoing maintenance.
Integration with Electrical Services
Earthing testing is integral to:
-
Substation Design: Soil resistivity and earth resistance data guide grounding grid layouts to meet safety standards.
-
Testing & Commissioning: Verifies grounding system installation before energization.
-
High Voltage O&M: Detects faults early to ensure continuous safe operation.
-
Solar Farm Services: Maintains grounding integrity for renewable energy safety.
-
Power System Analysis: Uses earthing data for accurate fault and load modeling.
-
High Voltage Testing and Protection & Control: Grounding is essential for protective device operation.
-
3D Digital Substation Designs: Incorporate earthing data for precise modeling and simulation.
Conclusion
Accurate earthing testing methods for electrical safety are fundamental to the reliable operation of substations, industrial plants, and renewable energy systems. Techniques such as soil resistivity testing, fall-of-potential procedures, selective earth ground testing, and stakeless methods provide comprehensive assessment of grounding systems. Portable devices and ASTM-compliant techniques empower engineers to maintain safety and compliance.



















































































































![Are AI Chatbots Replacing Search Engines? AI vs Google [New Research]](https://www.orbitmedia.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/How-often-are-we-using-AI-chatbots_.webp)































