CNC Turning Services: Precision Engineering for Modern Manufacturing
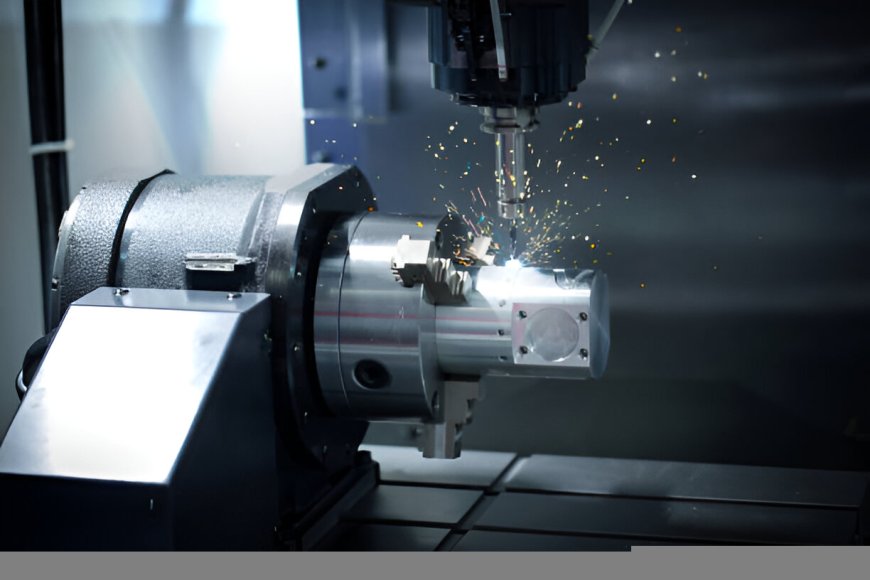

In today’s fast-paced and competitive manufacturing industry, CNC turning services have become a cornerstone for producing high-precision cylindrical parts with consistent accuracy. Businesses across aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics sectors rely on CNC turning services to meet demanding specifications, tight tolerances, and fast lead times without sacrificing quality.
What Are CNC Turning Services?
CNC turning is a subtractive manufacturing process in which a cutting tool removes material from a rotating workpiece to create cylindrical components. This operation is typically performed on a CNC lathe or turning center. Unlike manual turning, CNC turning services are automated and controlled by computer-generated code, resulting in faster production, greater repeatability, and higher precision.
These services are especially suited for creating parts like:
-
Shafts
-
Pins
-
Bushings
-
Screws
-
Connectors
Whether it’s a single prototype or a high-volume production run, CNC turning is efficient, cost-effective, and ideal for complex geometries that require precision and repeatability.
How CNC Turning Works
CNC turning starts with a digital design created using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The design is then converted into G-code via CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software, which instructs the machine how to operate.
Key steps in the CNC turning process:
-
Mounting the Workpiece: The raw material is secured in the lathe’s chuck.
-
Rotation: The workpiece spins on its axis while the cutting tool moves linearly.
-
Tooling Operations: Various tools are applied to shape the part by cutting, grooving, facing, drilling, or threading.
-
Part Removal: Once completed, the finished component is removed for inspection and possible post-processing.
Types of CNC Turning Operations
CNC turning isn't limited to a single machining action. Multiple specialized operations can be performed within one setup, maximizing efficiency and precision.
1. Facing
-
The tool moves perpendicular to the axis, creating a flat surface on the end of the part.
2. Grooving
-
Produces narrow slots or channels on the outside or inside diameter of the part.
3. Threading
-
Threads can be added to the internal or external surface using helical tool paths.
4. Drilling and Boring
-
Drilling creates holes, while boring enlarges them for better accuracy or tighter tolerances.
5. Parting (Cut-Off)
-
This operation separates the finished part from the remaining stock material.
CNC Turning Machines and Tools
Modern CNC turning centers come with advanced features that enhance both performance and versatility.
Lathe Types
-
2-Axis CNC Lathes: Basic turning and facing operations.
-
Multi-Axis Turning Centers (e.g., 3, 4, or 5-axis): Allow for milling, drilling, and complex part geometries in a single setup.
-
Swiss-Type Lathes: Ideal for small, high-precision parts often used in the medical and electronics industries.
Tooling Systems
-
Cutting tools are typically made from carbide, high-speed steel (HSS), or ceramics for strength and durability.
-
Quick-change tooling systems reduce downtime and boost productivity.
Benefits of CNC Turning Services
CNC turning offers a wide range of benefits that make it the go-to solution for precision manufacturing.
1. Precision and Accuracy
-
CNC turning machines achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.0002 inches.
2. Efficiency
-
Automated processes reduce cycle times and eliminate manual errors.
3. Repeatability
-
The same specifications can be reproduced over and over with near-zero variance.
4. Scalability
-
CNC turning services can efficiently handle low-volume prototypes or high-volume production runs.
5. Material Flexibility
-
Capable of machining a variety of metals (aluminum, steel, titanium) and plastics (PTFE, nylon, PEEK).
6. Lower Labor Costs
-
Fewer operators are needed since most of the work is automated.
Industries That Rely on CNC Turning Services
CNC turning is a critical manufacturing method across multiple industries:
Aerospace
-
High-performance, lightweight components like shafts, landing gear parts, and fasteners.
Automotive
-
Engine parts, pistons, and transmission components where durability and precision are crucial.
Medical
-
Surgical instruments and implant components that require extreme accuracy and biocompatibility.
Electronics
-
Miniaturized parts such as connectors, sensor housings, and micro-fasteners.
Industrial Machinery
-
Custom tools, gear shafts, and housings used in automation systems and heavy equipment.
How to Choose the Right CNC Turning Services Provider
Selecting the right partner is essential for product quality, turnaround time, and long-term success.
1. Experience and Expertise
-
Choose a provider with proven success in your industry and with similar components.
2. Certifications
-
Look for ISO 9001, AS9100, or IATF 16949 certifications to ensure strict quality standards.
3. Equipment Capabilities
-
Ensure the shop has multi-axis turning centers and can handle your required tolerances and materials.
4. Material Handling
-
Providers should have access to and experience with the materials your parts require.
5. Quality Assurance
-
In-process inspections, CMMs (Coordinate Measuring Machines), and detailed reporting ensure defect-free production.
6. Lead Time and Capacity
-
Make sure the provider can meet your deadlines and scale up if necessary.
Tips to Optimize Your CNC Turning Project
Before sending your part files for machining, keep these design and planning tips in mind to reduce cost and increase efficiency:
-
Simplify Complex Features: Avoid unnecessary undercuts and grooves that complicate tool paths.
-
Standardize Tolerances: Don’t call for ultra-tight tolerances unless absolutely needed.
-
Select Cost-Effective Materials: Match materials to the application instead of defaulting to exotic or expensive alloys.
-
Bundle Orders: Group multiple parts into a single run to reduce setup and handling time.
-
Use Design for Manufacturability (DFM): Consult with your provider for engineering input on cost-saving improvements.
Common Materials Used in CNC Turning
Here’s a breakdown of some popular materials used in CNC turning services and their typical applications:
|
Material |
Application Area |
Characteristics |
|
Aluminum |
Aerospace, Automotive |
Lightweight, corrosion-resistant |
|
Stainless Steel |
Medical, Industrial, Food Equipment |
Strong, durable, rust-resistant |
|
Brass |
Electronics, Plumbing |
Easy to machine, corrosion-resistant |
|
Titanium |
Aerospace, Medical |
Strong, biocompatible, heat-resistant |
|
Plastics (e.g., PEEK, Nylon) |
Electronics, Medical |
Lightweight, chemically resistant |
Future Trends in CNC Turning Services
As technology evolves, CNC turning is becoming smarter, faster, and even more accurate.
Smart Machining
-
Integration of sensors and IoT allows real-time monitoring for improved quality control.
AI and Machine Learning
-
Predictive tool wear analysis and adaptive machining strategies are reducing downtime.
Hybrid Machining Centers
-
Machines that combine turning, milling, and 3D printing are creating new possibilities in part design.
Sustainable Practices
-
Coolant recycling, energy-efficient machines, and minimal waste machining are becoming the norm.
Conclusion
CNC turning services are vital for any business that requires precision-machined, cylindrical components. With benefits like exceptional accuracy, material versatility, and scalability, CNC turning is an essential process in modern manufacturing. Whether you’re producing one part or one million, the right CNC partner can help you deliver consistent quality at competitive pricing.