Why is Building Self-Regulation Skills Important?
Attentio is a mobile app designed to help develop executive function and emotional regulation skills in individuals of all ages. This app will assist people in providing personalised care and timely support to their loved ones who need help handling their emotions, staying focused, exercising self-control, being organised, etc.

Basic Self-Regulation Skill
Cultivating and developing one's ability to self-regulate is certainly beneficial for long-term achievement. Here are some of the key self-regulation skills that teachers can directly promote in the classroom:
-
Emotion Awareness and Expression
Classes are a great place to learn about emotions, so that students can better manage their relationships with others and navigate their challenges. Educators can facilitate this process, for example, by providing opportunities to have open conversations about feelings and role-play scenarios that allow students to talk about and practice various emotional regulation. They may also use visual representations, such as emotion charts, to promote awareness of and language about emotions.
-
Impulse Control
Impulse control is an essential self-regulation skill because it allows students to stop and think before doing something; ultimately, the more students can use better judgment rather than impulsivity in making decisions, the more easily they will be able to resolve conflicts. Some examples of activities that can promote impulse control are freeze dance games and various waiting activities, where students learn about the benefits of hanging in there, and that some outcomes require some patience.
-
Anger Management
To create a positive environment in the classroom, it is important to manage anger. Showing self-regulation strategies such as deep-breathing, counting to ten or using ‘I’ statements are examples of ways you can help students regulate their feelings of anger and decrease negative behaviours.
-
Mindfulness
Mindfulness encourages focusing on the present moment, which can help students maintain their concentration and calmness. Simple mindfulness activities like breathing for attention (also known as conscious breathing) or guided imagery activities work well in a school setting. This will improve students’ ability to deal with stress and disengagement from the learning task.
-
Empathy
Building empathy helps students develop an appreciation for others' feelings and to respect those feelings, too. This builds healthy relationships. Experiment with activities that encourage perspective-taking, such as reading stories with characters or situations that have different emotions and motivations.
-
Resilience
Resilience is the ability to recover from adversity and is a necessary quality for students to persevere through challenges and failures. Resilience can be taught through the development of a growth mindset, emphasising positive self-talk, and through problem-solving activities.
-
Time Management
With time management, students can prioritise and complete tasks within time limits. Start by using planners or digital apps that are developmentally appropriate so that students can plan and schedule their tasks. Talk about deadlines, plan some timed activities and ask students to reflect regularly on how they used or are going to use their time; this builds understanding.
-
Stress Management
Stress management helps students to recognise stress and create coping skills for their mental health. Educate students to deal with stress through graduated muscle relaxation, visualisation exercises, or journaling. Having an open conversation about their issues can also help to identify stress sources and relieve stress.
-
Goal-setting
Educators can lead goal-setting meetings, in which students describe possible goals for themselves personally or academically, and goals that are achievable. Students can be motivated to think of both types of goals, whether it can be short-term or long-term. This will allow them to understand goal, plan, and decision-making, and build the ability to take steps to achieve these goals.
-
Self-compassion
Teaching students how to be kind to themselves when they fail or struggle is instrumental in forming a positive self-concept. Use activities that emphasise the importance of loving oneself, advocating for growth over perfection, understanding the role of mistakes in improving learning opportunities moving forward, etc.
Now that you have learn the basics of self-regulation, it’s time to know what kind of challenges one has to face while learning self-regulation.
Challenges with Teaching Self-Regulation
It is no easy feat to teach self-regulation. There are many common challenges faced by educators, parents, and policymakers. Overall, we can identify common challenges in four broad categories: institutional barriers, individual factors, pedagogical challenges, and environmental variables towards mitigating the sources of their stress.
-
Each student has their unique characteristics that become significant factors as self-regulation skills vary in students. Self-regulation skills are not something that some receive on their own, but they differ in a continuation of some degree or another. Attention spans and emotional maturity may differ immensely from one learner to the next, and these natural differences may make it difficult to implement strategies effectively for all students.
-
Pupils' social-emotional development may also be shaped by outside factors such as family or peer variables beyond the purview of the classroom. These outside factors can often work against the development we have put into the school, and to some degree, this creates inconsistency in what and when pupils develop.
-
Curricula loaded with core academic content often push personal growth concerns, such as learning self-regulation skills, to the periphery due to time and/or standardised testing constraints.
-
Some teachers may not have a robust understanding of these important skills in the first place because of a lack of professional development to support their learning in this area, which also hampers their teaching efforts.
Visit For More Info:-Attentio App
In conclusion, the most important thing to do is to create a safe and supportive environment for your child to learn to employ self-regulation skills to experience success in life. This is especially true if the child experiences sensory overload or has executive function concerns. Regardless of whether you are a parent, educator, or a combination of both, you have the job of hopefully promoting self-awareness for your child and providing feedback to help your child learn how to manage their frustration through new strategies.

































































![https //g.co/recover for help [1-866-719-1006]](https://newsquo.com/uploads/images/202506/image_430x256_684949454da3e.jpg)




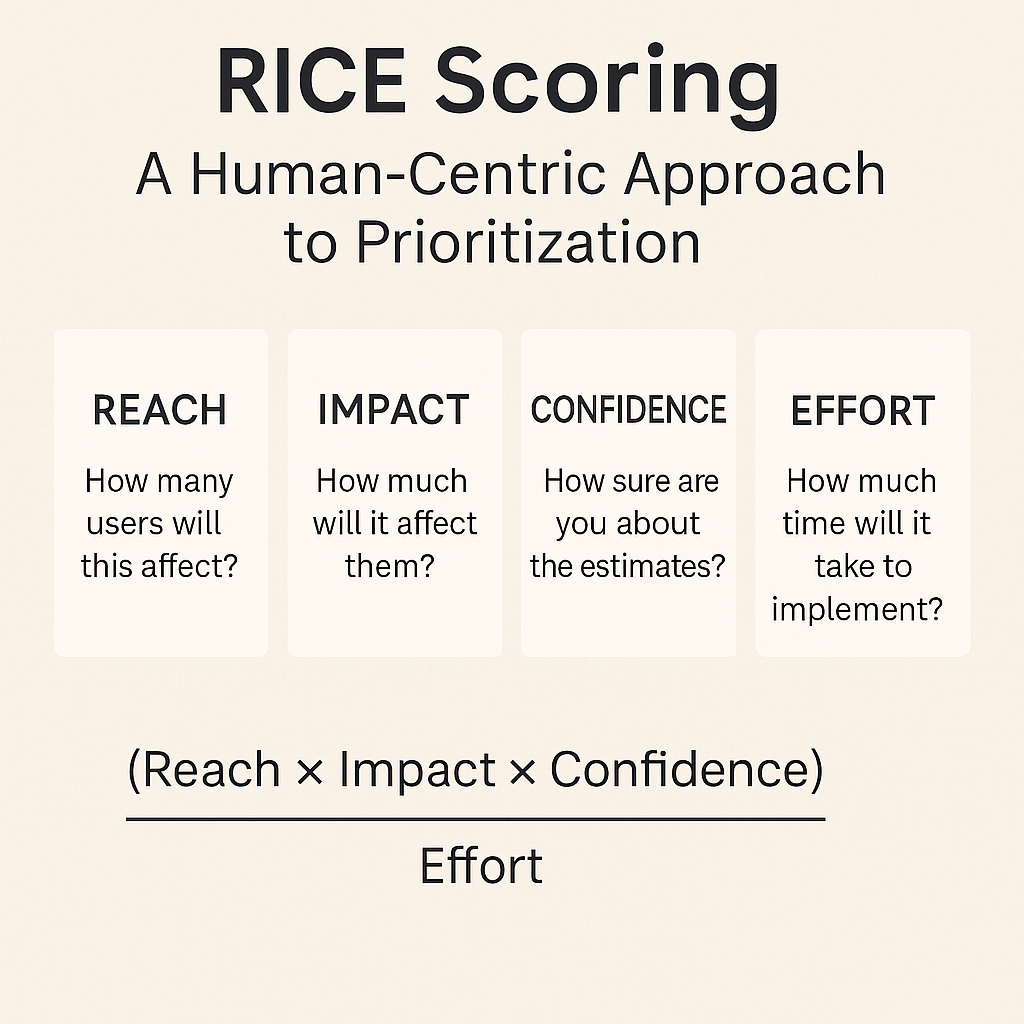




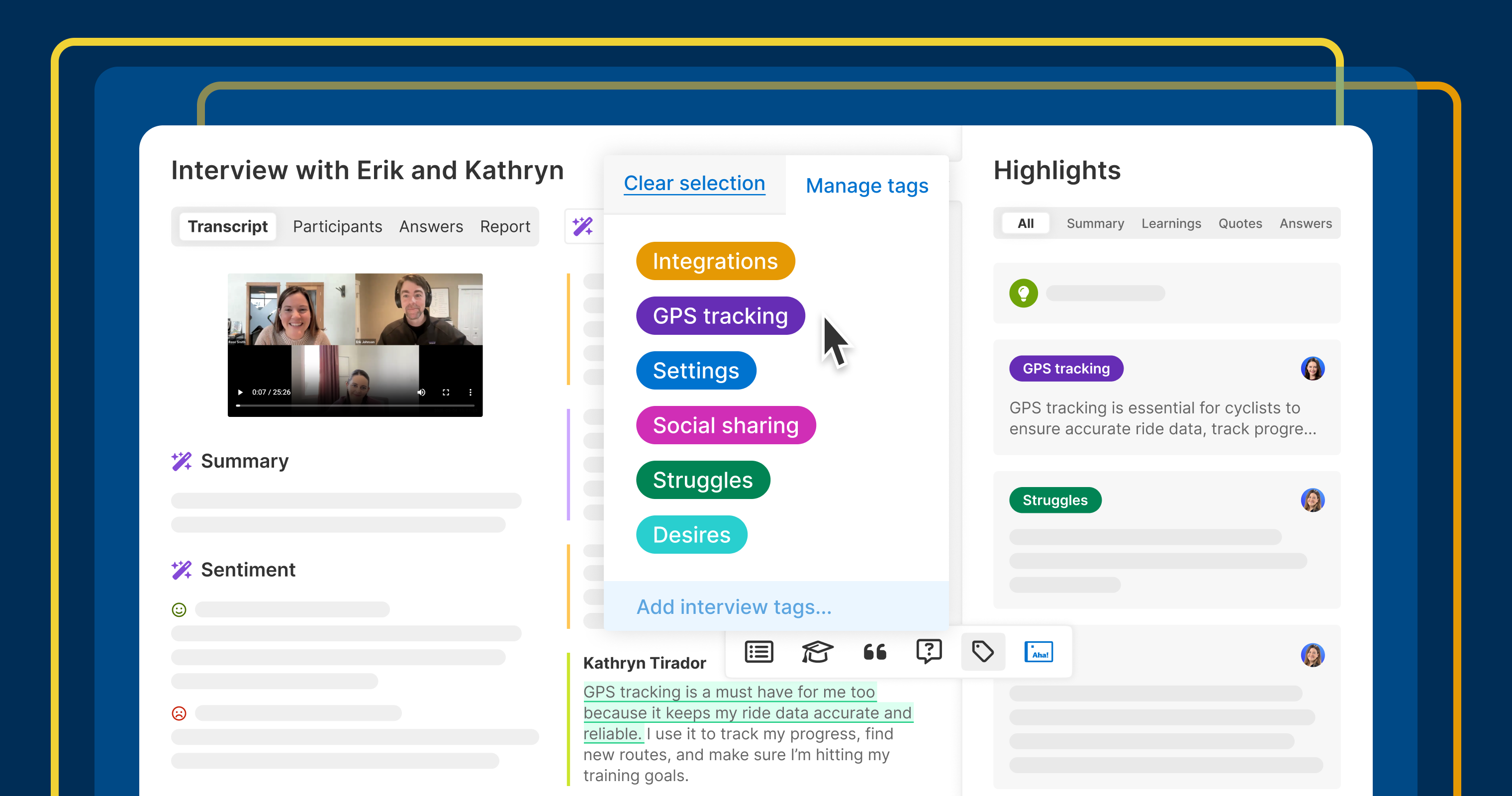










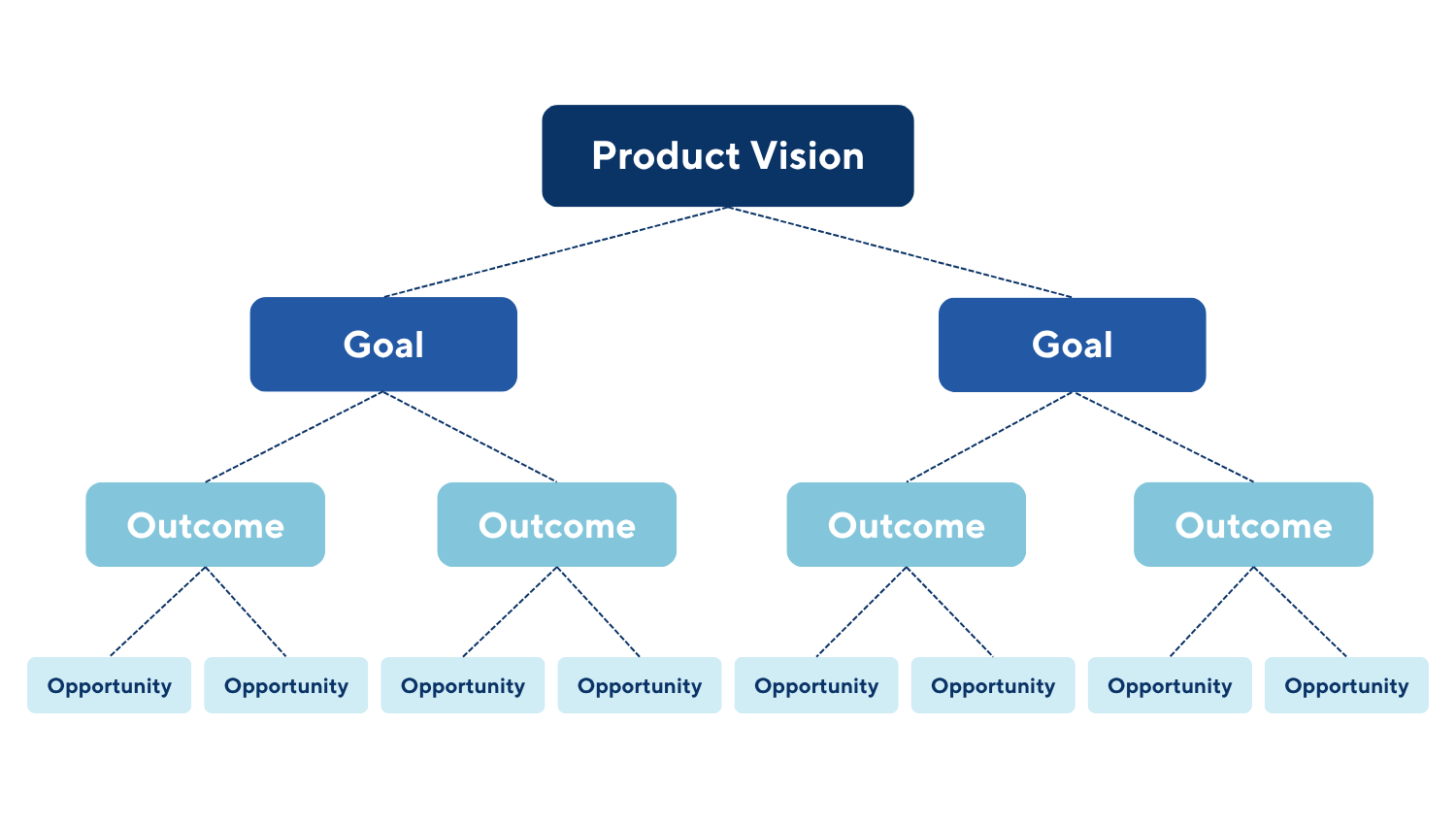



![How Smart PMs Scale Their Careers in Any Org [TPG Live Recap]](https://tpgblog.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/2025-06-12-thumbnail-action.png?#)



















































